Type 1 interferons and Foxo1 down-regulation play a key role in age-related T-cell exhaustion in mice
- PMID: 38409097
- PMCID: PMC10897180
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-45984-8
Type 1 interferons and Foxo1 down-regulation play a key role in age-related T-cell exhaustion in mice
Abstract
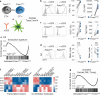
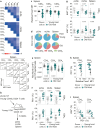
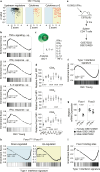
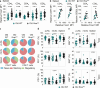
Foxo family transcription factors are critically involved in multiple processes, such as metabolism, quiescence, cell survival and cell differentiation. Although continuous, high activity of Foxo transcription factors extends the life span of some species, the involvement of Foxo proteins in mammalian aging remains to be determined. Here, we show that Foxo1 is down-regulated with age in mouse T cells. This down-regulation of Foxo1 in T cells may contribute to the disruption of naive T-cell homeostasis with age, leading to an increase in the number of memory T cells. Foxo1 down-regulation is also associated with the up-regulation of co-inhibitory receptors by memory T cells and exhaustion in aged mice. Using adoptive transfer experiments, we show that the age-dependent down-regulation of Foxo1 in T cells is mediated by T-cell-extrinsic cues, including type 1 interferons. Taken together, our data suggest that type 1 interferon-induced Foxo1 down-regulation is likely to contribute significantly to T-cell dysfunction in aged mice.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

