NINJ1 mediates inflammatory cell death, PANoptosis, and lethality during infection conditions and heat stress
- PMID: 38409108
- PMCID: PMC10897308
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-45466-x
NINJ1 mediates inflammatory cell death, PANoptosis, and lethality during infection conditions and heat stress
Abstract
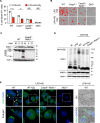
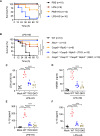
Innate immunity provides the first line of defense through multiple mechanisms, including pyrogen production and cell death. While elevated body temperature during infection is beneficial to clear pathogens, heat stress (HS) can lead to inflammation and pathology. Links between pathogen exposure, HS, cytokine release, and inflammation have been observed, but fundamental innate immune mechanisms driving pathology during pathogen exposure and HS remain unclear. Here, we use multiple genetic approaches to elucidate innate immune pathways in infection or LPS and HS models. Our results show that bacteria and LPS robustly increase inflammatory cell death during HS that is dependent on caspase-1, caspase-11, caspase-8, and RIPK3 through the PANoptosis pathway. Caspase-7 also contributes to PANoptosis in this context. Furthermore, NINJ1 is an important executioner of this cell death to release inflammatory molecules, independent of other pore-forming executioner proteins, gasdermin D, gasdermin E, and MLKL. In an in vivo HS model, mortality is reduced by deleting NINJ1 and fully rescued by deleting key PANoptosis molecules. Our findings suggest that therapeutic strategies blocking NINJ1 or its upstream regulators to prevent PANoptosis may reduce the release of inflammatory mediators and benefit patients.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
T.-D.K. was a consultant for Pfizer. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
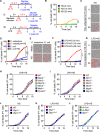
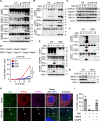
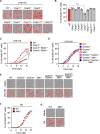
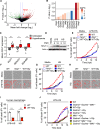
References
-
- El-Radhi, A. S. Clinical Manual of Fever in Children, 53–68 (2019).
-
- Hasday JD, Fairchild KD, Shanholtz C. The role of fever in the infected host. Microbes Infect. 2000;2:1891–1904. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R35 CA253095/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- AR056296/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- AI124346/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- R01 AI124346/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AI101935/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI160179/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI160179/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- N/A/American Lebanese Syrian Associated Charities (ALSAC)
- AI101935/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- R01 AR056296/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- CA253095/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | National Institutes of Health (NIH)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

