Biocatalytic cascade to polysaccharide amination
- PMID: 38409122
- PMCID: PMC10898118
- DOI: 10.1186/s13068-024-02477-6
Biocatalytic cascade to polysaccharide amination
Abstract
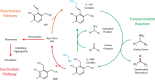
Background: Chitin, the main form of aminated polysaccharide in nature, is a biocompatible, polycationic, and antimicrobial biopolymer used extensively in industrial processes. Despite the abundance of chitin, applications thereof are hampered by difficulties in feedstock harvesting and limited structural versatility. To address these problems, we proposed a two-step cascade employing carbohydrate oxidoreductases and amine transaminases for plant polysaccharide aminations via one-pot reactions. Using a galactose oxidase from Fusarium graminearum for oxidation, this study compared the performance of CvATA (from Chromobacterium violaceum) and SpATA (from Silicibacter pomeroyi) on a range of oxidized carbohydrates with various structures and sizes. Using a rational enzyme engineering approach, four point mutations were introduced on the SpATA surface, and their effects on enzyme activity were evaluated.
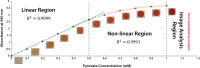
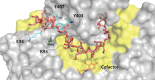
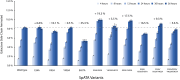
Results: Herein, a quantitative colorimetric assay was developed to enable simple and accurate time-course measurement of the yield of transamination reactions. With higher operational stability, SpATA produced higher product yields in 36 h reactions despite its lower initial activity. Successful amination of oxidized galactomannan by SpATA was confirmed using a deuterium labeling method; higher aminated carbohydrate yields achieved with SpATA compared to CvATA were verified using HPLC and XPS. By balancing the oxidase and transaminase loadings, improved operating conditions were identified where the side product formation was largely suppressed without negatively impacting the product yield. SpATA mutants with multiple alanine substitutions besides E407A showed improved product yield. The E407A mutation reduced SpATA activity substantially, supporting its predicted role in maintaining the dimeric enzyme structure.
Conclusions: Using oxidase-amine transaminase cascades, the study demonstrated a fully enzymatic route to polysaccharide amination. Although the activity of SpATA may be further improved via enzyme engineering, the low operational stability of characterized amine transaminases, as a result of low retention of PMP cofactors, was identified as a key factor limiting the yield of the designed cascade. To increase the process feasibility, future efforts to engineer improved SpATA variants should focus on improving the cofactor affinity, and thus the operational stability of the enzyme.
Keywords: Aminated polysaccharide; Amine transaminases; Enzymatic cascade; Transaminase activity assay.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Biocatalytic Production of Amino Carbohydrates through Oxidoreductase and Transaminase Cascades.ChemSusChem. 2019 Feb 21;12(4):848-857. doi: 10.1002/cssc.201802580. Epub 2019 Jan 29. ChemSusChem. 2019. PMID: 30589228 Free PMC article.
-
Amination of ω-Functionalized Aliphatic Primary Alcohols by a Biocatalytic Oxidation-Transamination Cascade.ChemCatChem. 2015 Oct;7(19):3121-3124. doi: 10.1002/cctc.201500589. Epub 2015 Sep 3. ChemCatChem. 2015. PMID: 26583050 Free PMC article.
-
Role of L-alanine for redox self-sufficient amination of alcohols.Microb Cell Fact. 2015 Jan 23;14:9. doi: 10.1186/s12934-014-0189-x. Microb Cell Fact. 2015. PMID: 25612558 Free PMC article.
-
High-Yield Synthesis of Enantiopure 1,2-Amino Alcohols from l-Phenylalanine via Linear and Divergent Enzymatic Cascades.Org Process Res Dev. 2022 Jul 15;26(7):2085-2095. doi: 10.1021/acs.oprd.1c00490. Epub 2022 Mar 28. Org Process Res Dev. 2022. PMID: 35873603 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biocatalytic concepts for synthesizing amine bulk chemicals: recent approaches towards linear and cyclic aliphatic primary amines and ω-substituted derivatives thereof.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2019 Jan;103(1):83-95. doi: 10.1007/s00253-018-9452-0. Epub 2018 Oct 26. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2019. PMID: 30367182 Review.
References
-
- Lichtfouse E, Morin-Crini N, Fourmentin M, Zemmouri H, do Carmo Nascimento IO, Queiroz LM, et al. Chitosan for direct bioflocculation of wastewater. Environ Chem Lett. 2019;17:1603–1621. doi: 10.1007/s10311-019-00900-1. - DOI
-
- Morin-Crini N, Lichtfouse E, Torri G, Crini G. Applications of chitosan in food, pharmaceuticals, medicine, cosmetics, agriculture, textiles, pulp and paper, biotechnology, and environmental chemistry. Environ Chem Lett. 2019;17:1667–1692. doi: 10.1007/s10311-019-00904-x. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
