Shaping high-performance wearable robots for human motor and sensory reconstruction and enhancement
- PMID: 38409128
- PMCID: PMC10897332
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-46249-0
Shaping high-performance wearable robots for human motor and sensory reconstruction and enhancement
Abstract
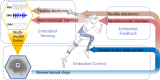
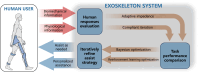
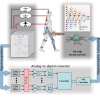
Most wearable robots such as exoskeletons and prostheses can operate with dexterity, while wearers do not perceive them as part of their bodies. In this perspective, we contend that integrating environmental, physiological, and physical information through multi-modal fusion, incorporating human-in-the-loop control, utilizing neuromuscular interface, employing flexible electronics, and acquiring and processing human-robot information with biomechatronic chips, should all be leveraged towards building the next generation of wearable robots. These technologies could improve the embodiment of wearable robots. With optimizations in mechanical structure and clinical training, the next generation of wearable robots should better facilitate human motor and sensory reconstruction and enhancement.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

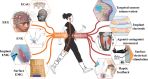

Similar articles
-
Evaluating the effectiveness of an active strap for wearable robot: A Mechanical and Physiological Study.Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2023 Jul;2023:1-6. doi: 10.1109/EMBC40787.2023.10340474. Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2023. PMID: 38083124
-
User-Centered Evaluation of the Wearable Walker Lower Limb Exoskeleton; Preliminary Assessment Based on the Experience Protocol.Sensors (Basel). 2024 Aug 19;24(16):5358. doi: 10.3390/s24165358. Sensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39205050 Free PMC article.
-
Wearable Biofeedback Improves Human-Robot Compliance during Ankle-Foot Exoskeleton-Assisted Gait Training: A Pre-Post Controlled Study in Healthy Participants.Sensors (Basel). 2020 Oct 17;20(20):5876. doi: 10.3390/s20205876. Sensors (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33080845 Free PMC article.
-
Review on Portable-Powered Lower Limb Exoskeletons.Sensors (Basel). 2024 Dec 18;24(24):8090. doi: 10.3390/s24248090. Sensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39771825 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Systematic review on wearable lower-limb exoskeletons for gait training in neuromuscular impairments.J Neuroeng Rehabil. 2021 Feb 1;18(1):22. doi: 10.1186/s12984-021-00815-5. J Neuroeng Rehabil. 2021. PMID: 33526065 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Effect of Wearable Exoskeleton Robots on Muscle Activation and Gait Parameters on a Treadmill: A Randomized Controlled Trial.Healthcare (Basel). 2025 Mar 22;13(7):700. doi: 10.3390/healthcare13070700. Healthcare (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40217998 Free PMC article.
-
A systematic literature review on integrating AI-powered smart glasses into digital health management for proactive healthcare solutions.NPJ Digit Med. 2025 Jul 5;8(1):410. doi: 10.1038/s41746-025-01715-x. NPJ Digit Med. 2025. PMID: 40617964 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Advances in Conductive Hydrogels for Electronic Skin and Healthcare Monitoring.Biosensors (Basel). 2025 Jul 18;15(7):463. doi: 10.3390/bios15070463. Biosensors (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40710112 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Soft, Stretchable, High-Sensitivity, Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotube-Based Strain Sensor for Joint Healthcare.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2025 Feb 21;15(5):332. doi: 10.3390/nano15050332. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40072135 Free PMC article.
-
Soft Robotics for Parkinson's Disease Supported by Functional Materials and Artificial Intelligence.BME Front. 2025 Jul 2;6:0143. doi: 10.34133/bmef.0143. eCollection 2025. BME Front. 2025. PMID: 40606522 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Serino A, et al. Upper limb cortical maps in amputees with targeted muscle and sensory reinnervation. Brain. 2017;140:2993–3011. - PubMed
-
- Fritsch A, Lenggenhager B, Bekrater-Bodmann R. Prosthesis embodiment and attenuation of prosthetic touch in upper limb amputees – A proof-of-concept study. Conscious Cogn. 2021;88:103073. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

