Associations between Th1-related cytokines and complicated pediatric appendicitis
- PMID: 38409170
- PMCID: PMC10897334
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-53756-z
Associations between Th1-related cytokines and complicated pediatric appendicitis
Abstract
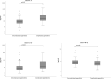
The pathogenesis of appendicitis is not understood fully, and the diagnosis can be challenging. Previous research has suggested an association between a T helper (Th) 1-dependent immune response and complicated appendicitis. This prospective cohort study aimed to evaluate the association between serum concentrations of the Th1-associated cytokines interleukin (IL)-1α, IL-1β, IL-2, IL-6, IL-10, IL-17A and tumor necrosis factor beta (TNF-β) and the risk of complicated appendicitis in children. Appendicitis severity was determined through histopathological examination. A total of 137 children < 15 years with appendicitis were included with a median age of 10 years (IQR 8-12); 86 (63%) were boys, and 58 (42%) had complicated appendicitis. Children with complicated appendicitis had significantly higher concentrations of serum IL-6 and IL-10, and lower of TNF-β. After adjustment for age, symptom duration, and presence of appendicolith in a multivariable logistic regression, a higher concentration of IL-6 remained associated with an increased risk of complicated appendicitis (aOR 1.001 [95% CI 1.000-1.002], p = 0.02). Serum concentrations of IL-1α, IL-1β, IL-2, IL-10, IL-17A and TNF-β were not significantly associated with the risk of complicated appendicitis. In conclusion, our results suggests that the systemic inflammatory response in complicated appendicitis is complex and not solely Th1-dependent.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Andersson RE. The natural history and traditional management of appendicitis revisited: Spontaneous resolution and predominance of prehospital perforations imply that a correct diagnosis is more important than an early diagnosis. World J. Surg. 2007;31:86–92. doi: 10.1007/s00268-006-0056-y. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical