When temporal attention interacts with expectation
- PMID: 38409235
- PMCID: PMC10897459
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-55399-6
When temporal attention interacts with expectation
Abstract
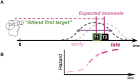
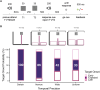
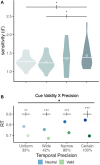
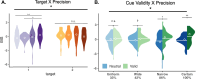
Temporal attention is voluntarily deployed at specific moments, whereas temporal expectation is deployed according to timing probabilities. When the target appears at an expected moment in a sequence, temporal attention improves performance at the attended moments, but the timing and the precision of the attentional window remain unknown. Here we independently and concurrently manipulated temporal attention-via behavioral relevance-and temporal expectation-via session-wise precision and trial-wise hazard rate-to investigate whether and how these mechanisms interact to improve perception. Our results reveal that temporal attention interacts with temporal expectation-the higher the precision, the stronger the attention benefit, but surprisingly this benefit decreased with delayed onset despite the increasing probability of stimulus appearance. When attention was suboptimally deployed to earlier than expected moments, it could not be reoriented to a later time point. These findings provide evidence that temporal attention and temporal expectation are different mechanisms, and highlight their interplay in optimizing visual performance.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Probability-driven and stimulus-driven orienting of attention to time and sensory modality.Atten Percept Psychophys. 2019 Nov;81(8):2732-2744. doi: 10.3758/s13414-019-01798-1. Atten Percept Psychophys. 2019. PMID: 31254259 Free PMC article.
-
The Spatiotemporal Link of Temporal Expectations: Contextual Temporal Expectation Is Independent of Spatial Attention.J Neurosci. 2022 Mar 23;42(12):2516-2523. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1555-21.2022. Epub 2022 Jan 28. J Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35091506 Free PMC article.
-
Motivation alters implicit temporal attention through sustained and transient mechanisms: A behavioral and pupillometric study.Psychophysiology. 2018 Dec;55(12):e13275. doi: 10.1111/psyp.13275. Epub 2018 Aug 17. Psychophysiology. 2018. PMID: 30120780
-
The Intricate Interplay of Spatial Attention and Expectation: a Multisensory Perspective.Multisens Res. 2020 Mar 17;33(4-5):383-416. doi: 10.1163/22134808-20201482. Multisens Res. 2020. PMID: 31940592 Review.
-
Evaluating the evidence for expectation suppression in the visual system.Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2021 Jul;126:368-381. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2021.04.002. Epub 2021 Apr 6. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2021. PMID: 33836212 Review.
Cited by
-
Temporal attention and oculomotor effects dissociate distinct types of temporal expectation.J Vis. 2025 Aug 1;25(10):3. doi: 10.1167/jov.25.10.3. J Vis. 2025. PMID: 40762532 Free PMC article.
-
Temporal context modulates the recovery of the attentional blink.Cogn Res Princ Implic. 2025 Mar 28;10(1):14. doi: 10.1186/s41235-025-00625-6. Cogn Res Princ Implic. 2025. PMID: 40153193 Free PMC article.
-
Eyes on the past: Gaze stability differs between temporal expectation and temporal attention.J Vis. 2025 Apr 1;25(4):11. doi: 10.1167/jov.25.4.11. J Vis. 2025. PMID: 40238139 Free PMC article.
-
Temporal attention and oculomotor effects dissociate distinct types of temporal expectation.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Mar 6:2025.03.04.641562. doi: 10.1101/2025.03.04.641562. bioRxiv. 2025. Update in: J Vis. 2025 Aug 1;25(10):3. doi: 10.1167/jov.25.10.3. PMID: 40093085 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Task demand mediates the interaction of spatial and temporal attention.Sci Rep. 2024 Apr 22;14(1):9228. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-58209-1. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38649675 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shapiro K. The limits of attention: temporal constraints in human information processing. 2001 doi: 10.1093/acprof:oso/9780198505150.001.0001. - DOI
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

