Multimodal detection of molecular residual disease in high-risk locally advanced squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck
- PMID: 38409276
- PMCID: PMC11043441
- DOI: 10.1038/s41418-024-01272-y
Multimodal detection of molecular residual disease in high-risk locally advanced squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck
Abstract
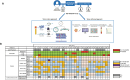
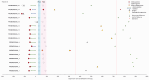
Up to 30% of patients with locally advanced head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (LA-HNSCC) relapse. Molecular residual disease (MRD) detection using multiple assays after definitive therapy has not been reported. In this study, we included patients with LA-HNSCC (stage III Human Papilloma virus (HPV)-positive, III-IVB HPV-negative) treated with curative intent. Plasma was collected pre-treatment, at 4-6 weeks (FU1) and 8-12 weeks (FU2) post-treatment. Circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) was analyzed using a tumor-informed (RaDaR®) and a tumor-naïve (CAPP-seq) assay. HPV DNA was measured using HPV-sequencing (HPV-seq) and digital PCR (dPCR). A total of 86 plasma samples from 32 patients were analyzed; all patients with at least 1 follow-up sample. Most patients were stage III HPV-positive (50%) and received chemoradiation (78%). No patients had radiological residual disease at FU2. With a median follow-up of 25 months, there were 7 clinical relapses. ctDNA at baseline was detected in 15/17 (88%) by RaDaR and was not associated with recurrence free survival (RFS). Two patients relapsed within a year after definitive therapy and showed MRD at FU2 using RaDaR; detection of ctDNA during follow-up was associated with shorter RFS (p < 0.001). ctDNA detection by CAPP-seq pre-treatment and during follow-up was not associated with RFS (p = 0.09). HPV DNA using HPV-seq or dPCR during follow-up was associated with shorter RFS (p < 0.001). Sensitivity and specificity for MRD at FU2 using RaDaR was 40% and 100% versus 20 and 90.5% using CAPP-seq. Sensitivity and specificity for MRD during follow-up using HPV-seq was 100% and 91.7% versus 50% and 100% using dPCR. In conclusion, HPV DNA and ctDNA can be detected in LA-HNSCC before definitive therapy. The RaDaR assay but not CAPP-seq may detect MRD in patients who relapse within 1 year. HPV-seq may be more sensitive than dPCR for MRD detection.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
ESG reported research funding from Novartis. JZ is Co-inventor of patent application pending related to detection of HPV circulating cell-free DNA. It is held by the institution and is not royalty generating. AS reported a consulting/advisory role with Merck and Bristol-Myers Squibb, and grant/research funding from Novartis, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Symphogen AstraZeneca/Medimmune, Merck, Bayer, Surface Oncology, Northern Biologics, Janssen Oncology/Johnson & Johnson, Roche, Regeneron, Alkermes, Array Biopharma/Pfizer, GSK, NuBiyota, Oncorus, Treadwell, Amgen, ALX Oncology, Nubiyota, Genentech, Seagen, Servier. AHansen reported receiving research funds to his institution from Karyopharm and Boston Biomedical and research funds to his institution and consulting/advising honoraria from Novartis, Genentech Inc, Hoffmann La Roche Inc, Merck Serono, GlaxoSmithKline, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Boehringer Ingelheim International, AstraZeneca, Medimmune, and Pfizer. ZZ is co-inventor of patent application pending related to detection of HPV circulating cell-free DNA. It is held by the institution and is not royalty generating. CS is employee of NeoGenomics Laboratories. Scott V Bratman reported being a co-inventor on patents relating to circulating tumor DNA technologies licensed to Roche and Adela, and is a cofounder of Adela in which he carries a leadership role. LLS reported a leadership role with Treadwell Therapeutics, stock or ownership interest in Agios, consulting/advisory role with Merck, AstraZeneca/MedImmune, Roche, Voronoi Health Analytics, Oncorus, GlaxoSmithKline, Seattle Genetics, Arvinas, Navire, Janpix, Relay Therapeutics, Daiichi Sankyo/UCB Japan, Janssen, Hookipa Pharma, InterRNA, Tessa Therapeutics, Sanofi, Amgen, and research funding from Bristol Myers Squibb (Inst), Genentech/Roche (Inst), GlaxoSmithKline (Inst), Merck (Inst), Novartis (Inst), Pfizer (Inst), AstraZeneca (Inst), Boehringer Ingelheim (Inst), Bayer (Inst), Amgen (Inst), Astellas Pharma (Inst), Shattuck Labs (Inst), Symphogen (Inst), AVID Radiopharmaceuticals (Inst), Mirati Therapeutics (Inst), Intensity Therapeutics (Inst), Karyopharm Therapeutics (Inst). The remaining authors did not declare any potential conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Machiels JP, Rene Leemans C, Golusinski W, Grau C, Licitra L, Gregoire V, et al. Squamous cell carcinoma of the oral cavity, larynx, oropharynx and hypopharynx: EHNS-ESMO-ESTRO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol. 2020;31:1462–75. doi: 10.1016/j.annonc.2020.07.011. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

