Sexual dimorphism during integrative endocrine and immune responses to ionizing radiation in mice
- PMID: 38409284
- PMCID: PMC10897391
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-33629-7
Sexual dimorphism during integrative endocrine and immune responses to ionizing radiation in mice
Abstract
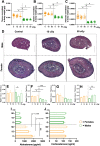
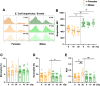
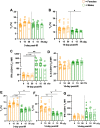
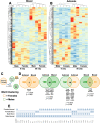
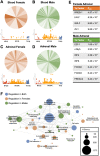
Exposure to cosmic ionizing radiation is an innate risk of the spaceflight environment that can cause DNA damage and altered cellular function. In astronauts, longitudinal monitoring of physiological systems and interactions between these systems are important to consider for mitigation strategies. In addition, assessments of sex-specific biological responses in the unique environment of spaceflight are vital to support future exploration missions that include both females and males. Here we assessed sex-specific, multi-system immune and endocrine responses to simulated cosmic radiation. For this, 24-week-old, male and female C57Bl/6J mice were exposed to simplified five-ion, space-relevant galactic cosmic ray (GCRsim) radiation at 15 and 50 cGy, to simulate predicted radiation exposures that would be experienced during lunar and Martian missions, respectively. Blood and adrenal tissues were collected at 3- and 14-days post-irradiation for analysis of immune and endocrine biosignatures and pathways. Sexually dimorphic adrenal gland weights and morphology, differential total RNA expression with corresponding gene ontology, and unique immune phenotypes were altered by GCRsim. In brief, this study offers new insights into sexually dimorphic immune and endocrine kinetics following simulated cosmic radiation exposure and highlights the necessity for personalized translational approaches for astronauts during exploration missions.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
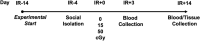
Similar articles
-
Sex-specific effects on the heart from combined exposure to simulated galactic cosmic radiation and hindlimb unloading.Life Sci Space Res (Amst). 2025 Feb;44:38-46. doi: 10.1016/j.lssr.2024.12.001. Epub 2024 Dec 6. Life Sci Space Res (Amst). 2025. PMID: 39864910
-
Getting ready for the manned mission to Mars: the astronauts' risk from space radiation.Naturwissenschaften. 2007 Jul;94(7):517-26. doi: 10.1007/s00114-006-0204-0. Epub 2007 Jan 19. Naturwissenschaften. 2007. PMID: 17235598 Review.
-
Similar Loss of Executive Function Performance after Exposure to Low (10 cGy) Doses of Single (4He) Ions and the Multi-Ion GCRSim Beam.Radiat Res. 2022 Oct 1;198(4):375-383. doi: 10.1667/RADE-22-00022.1. Radiat Res. 2022. PMID: 36223207
-
Health care for deep space explorers.Ann ICRP. 2020 Dec;49(1_suppl):182-184. doi: 10.1177/0146645320935288. Epub 2020 Jul 31. Ann ICRP. 2020. PMID: 32734760
-
The Effects of Cosmic Radiation Exposure on Pregnancy During a Probable Manned Mission to Mars.Life Sci Space Res (Amst). 2025 Feb;44:154-162. doi: 10.1016/j.lssr.2024.10.008. Epub 2024 Oct 28. Life Sci Space Res (Amst). 2025. PMID: 39864908 Review.
Cited by
-
Taking the 3Rs to a higher level: replacement and reduction of animal testing in life sciences in space research.Biotechnol Adv. 2025 Jul-Aug;81:108574. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2025.108574. Epub 2025 Apr 1. Biotechnol Adv. 2025. PMID: 40180136 Review.
-
To boldly go where no microRNAs have gone before: spaceflight impact on risk for small-for-gestational-age infants.Commun Biol. 2024 Oct 5;7(1):1268. doi: 10.1038/s42003-024-06944-6. Commun Biol. 2024. PMID: 39369042 Free PMC article.
-
A second space age spanning omics, platforms and medicine across orbits.Nature. 2024 Aug;632(8027):995-1008. doi: 10.1038/s41586-024-07586-8. Epub 2024 Jun 11. Nature. 2024. PMID: 38862027 Review.
-
Thymus ad astra, or spaceflight-induced thymic involution.Front Immunol. 2025 Jan 24;15:1534444. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1534444. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 39926601 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Crucian BE, Choukèr A, Simpson RJ, Mehta S, Marshall G, Smith SM, Zwart SR, Heer M, Ponomarev S, Whitmire A, Frippiat JP, Douglas GL, Lorenzi H, Buchheim JI, Makedonas G, Ginsburg GS, Ott CM, Pierson DL, Krieger SS, Baecker N, Sams C. Immune system dysregulation during spaceflight: potential countermeasures for deep space exploration missions. Front. Immunol. 2018;9:1437. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01437. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Rummell JA, Sawin CF, Buderer MC, Mauldin DG, Michel EL. Physiological response to exercise after space flight–Apollo 14 through Apollo 17. Aviat. Space Environ. Med. 1975;46:679–683. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

