Community detection with Greedy Modularity disassembly strategy
- PMID: 38409331
- PMCID: PMC10897298
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-55190-7
Community detection with Greedy Modularity disassembly strategy
Abstract
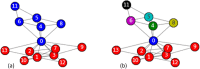
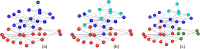
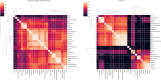
Community detection recognizes groups of densely connected nodes across networks, one of the fundamental procedures in network analysis. This research boosts the standard but locally optimized Greedy Modularity algorithm for community detection. We introduce innovative exploration techniques that include a variety of node and community disassembly strategies. These strategies include methods like non-triad creating, feeble, random as well as inadequate embeddedness for nodes, as well as low internal edge density, low triad participation ratio, weak, low conductance as well as random tactics for communities. We present a methodology that showcases the improvement in modularity across the wide variety of real-world and synthetic networks over the standard approaches. A detailed comparison against other well-known community detection algorithms further illustrates the better performance of our improved method. This study not only optimizes the process of community detection but also broadens the scope for a more nuanced and effective network analysis that may pave the way for more insights as to the dynamism and structures of its functioning by effectively addressing and overcoming the limitations that are inherently attached with the existing community detection algorithms.
Keywords: Community detection; Disassembly greedy; Greedy Modularity.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures










References
-
- Barabási A-L. Network Science. Cambridge University Press; 2016.
-
- Shang KK, Small M, Wang Y, Yin D, Li S. A novel metric for community detection. Europhys. Lett. 2020;129:68002. doi: 10.1209/0295-5075/129/68002. - DOI
-
- Chakraborty T, Dalmia A, Mukherjee A, Ganguly N. Metrics for community analysis: A survey. ACM Comput. Surv. 2017;50:1–37. doi: 10.1145/3091106. - DOI
-
- Chen M, Kuzmin K, Szymanski BK. Community detection via maximization of modularity and its variants. IEEE Trans. Comput. Soc. Syst. 2014;1:46–65. doi: 10.1109/TCSS.2014.2307458. - DOI
-
- Zhu J, et al. A no self-edge stochastic block model and a heuristic algorithm for balanced anti-community detection in networks. Inf. Sci. 2020;518:95–112. doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2020.01.005. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

