Sinensetin suppresses breast cancer cell progression via Wnt/β-catenin pathway inhibition
- PMID: 38410229
- PMCID: PMC10894327
- DOI: 10.21037/tcr-23-1317
Sinensetin suppresses breast cancer cell progression via Wnt/β-catenin pathway inhibition
Abstract
Background: Although there are many treatments for breast cancer, such as surgery, radiotherapy, chemotherapy, estrogen receptor antagonists, immune checkpoint inhibitors and so on. However, safer and more effective therapeutic drugs for breast cancer are needed. Sinensetin, a safer therapeutic drugs, come from citrus species and medicinal plants used in traditional medicine, while its role and underlying mechanism in breast cancer remain unclear. Our study aimed to investigate the role and mechanism of sinensetin in breast cancer.
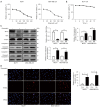
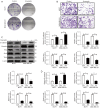
Methods: Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8) was used to determine the safe concentration of sinensetin in MCF-10A, MCF7 and MDA-MB-231 cells; 120 μM sinensetin was used in subsequent experiments. Real time polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR), Western blotting, Terminal Deoxynucleotidyl Transferase mediated dUTP Nick-End Labeling (TUNEL) apoptosis assay, Transwell invasion assay and Clone formation assay were used in this study to determine cell viability, mRNA expression, protein levels, apoptosis, proliferation, invasion and so on.
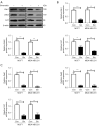
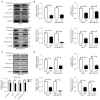
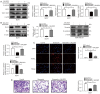
Results: Herein, our results showed that 120 μM sinensetin suppressed the cell viability and promoted apoptosis of MCF7 and MDA-MB-231 cells. Treatment with 120 µM sinensetin for 24 h showed no significant toxicity to normal mammary cells; 120 μM sinensetin decreased cell proliferation, invasion, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), and downregulated β-catenin, lymphatic enhancing factor 1 (LEF1), T-cell factor (TCF) 1/TCF7, and TCF3/TCF7L1 expression in MCF7 and MDA-MB-231 cells. The Wnt agonist SKL2001 reversed the inhibitory effect of sinensetin on cell survival, metastasis, and EMT. Sinensetin-induced downregulation of β-catenin, LEF1, and TCF1/TCF7 expression were upregulated by SKL2001 in MCF7 and MDA-MB-231 cells.
Conclusions: In summary, sinensetin suppressed the metastasis of breast cancer cell via inhibition of Wnt/β-catenin pathway and there were no adverse effects on normal breast cells. Our study confirmed the role of sinensetin in breast cancer cells and provided a better understanding of the underlying mechanism.
Keywords: Breast cancer; Wnt; apoptosis; epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT); sinensetin.
2024 Translational Cancer Research. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://tcr.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/tcr-23-1317/coif). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Baicalein suppresses metastasis of breast cancer cells by inhibiting EMT via downregulation of SATB1 and Wnt/β-catenin pathway.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2016 Apr 18;10:1419-41. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S102541. eCollection 2016. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2016. PMID: 27143851 Free PMC article.
-
FL118, a novel camptothecin analogue, suppressed migration and invasion of human breast cancer cells by inhibiting epithelial-mesenchymal transition via the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway.Biosci Trends. 2018;12(1):40-46. doi: 10.5582/bst.2017.01288. Biosci Trends. 2018. PMID: 29553100
-
Wnt/β-catenin pathway is required for epithelial to mesenchymal transition in CXCL12 over expressed breast cancer cells.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015 Oct 1;8(10):12357-67. eCollection 2015. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015. PMID: 26722422 Free PMC article.
-
The pan-inhibitor of Aurora kinases danusertib induces apoptosis and autophagy and suppresses epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in human breast cancer cells.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2015 Feb 17;9:1027-62. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S74412. eCollection 2015. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2015. PMID: 25733818 Free PMC article.
-
Apatinib Inhibits Stem Properties and Malignant Biological Behaviors of Breast Cancer Stem Cells by Blocking Wnt/β-catenin Signal Pathway through Downregulating LncRNA ROR.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2022;22(9):1723-1734. doi: 10.2174/1871520621666210412103849. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2022. PMID: 33845750
Cited by
-
Citrus flavonoids for overcoming breast cancer resistance to methotrexate: identification of potential targets of nobiletin and sinensetin.Discov Oncol. 2025 Mar 20;16(1):365. doi: 10.1007/s12672-025-02116-y. Discov Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40111633 Free PMC article.
-
A-to-I-edited miR-1251-5p restrains tumor growth and metastasis in lung adenocarcinoma through regulating TCF7-mediated Wnt signaling pathway.Discov Oncol. 2024 Oct 24;15(1):587. doi: 10.1007/s12672-024-01462-7. Discov Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39446175 Free PMC article.
-
FNDC1 Facilitates Proliferation, Migration, and Invasion of Breast Cancer Cells Through Modulating Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway.Biochem Genet. 2024 Dec 13. doi: 10.1007/s10528-024-10994-0. Online ahead of print. Biochem Genet. 2024. PMID: 39671143
-
Role of PARP Inhibitors: A New Hope for Breast Cancer Therapy.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Mar 19;26(6):2773. doi: 10.3390/ijms26062773. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40141415 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Flavonoids of Euphorbia hirta inhibit inflammatory mechanisms via Nrf2 and NF-κB pathways.Cell Biochem Biophys. 2025 Mar;83(1):1167-1183. doi: 10.1007/s12013-024-01551-y. Epub 2024 Nov 6. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2025. PMID: 39505796
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
