Nutritional, biochemical and health properties of Locust beans and its applications in the food industry: a review
- PMID: 38410274
- PMCID: PMC10894154
- DOI: 10.1007/s13197-023-05765-5
Nutritional, biochemical and health properties of Locust beans and its applications in the food industry: a review
Abstract
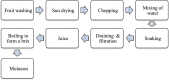
The Locust Bean (Ceratonia siliqua L.) is an ancient Mediterranean fruit that is used to make locust bean gum from seeds, which is a popular ingredient in many foods today. Locust Bean fruit and Gum are rich in bioactive compounds that can be helpful in the treatment of conditions involving the digestive system, as well as cancer, hyperlipidemia, and diabetes. The locust bean gum is a polysaccharide extracted from the endosperm of the locust bean seed through different thermomechanical or chemical processes. It is an approved food additive with the European number E410 and a number of different food uses. It is a galactomannan and it is frequently used in dairy products for its water-binding and thickening properties to improve their rheological properties. This review aims to study the functional, and nutritional characteristics of Locust Bean Gum, the extraction of Locust Bean Gum, as well as its applications in the food sector and its impacts on dairy product processing.
Supplementary information: The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1007/s13197-023-05765-5.
Keywords: Food applications; Locust bean gum; Physiochemical; Polysaccharides; Processing.
© Association of Food Scientists & Technologists (India) 2023. Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Locust bean gum: processing, properties and food applications--a review.Int J Biol Macromol. 2014 May;66:74-80. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2014.02.017. Epub 2014 Feb 16. Int J Biol Macromol. 2014. PMID: 24548746 Review.
-
Locust Bean Gum: Processing, Properties and Food Applications.Recent Adv Food Nutr Agric. 2022;13(2):93-102. doi: 10.2174/2772574X14666221107104357. Recent Adv Food Nutr Agric. 2022. PMID: 36345241
-
Re-evaluation of locust bean gum (E 410) as a food additive.EFSA J. 2017 Jan 20;15(1):e04646. doi: 10.2903/j.efsa.2017.4646. eCollection 2017 Jan. EFSA J. 2017. PMID: 32625248 Free PMC article.
-
Chemical characterization of carob seeds (Ceratonia siliqua L.) and use of different extraction techniques to promote its bioactivity.Food Chem. 2021 Jul 30;351:129263. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.129263. Epub 2021 Feb 13. Food Chem. 2021. PMID: 33631614
-
Locust Bean Gum, a Vegetable Hydrocolloid with Industrial and Biopharmaceutical Applications.Molecules. 2022 Nov 26;27(23):8265. doi: 10.3390/molecules27238265. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36500357 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Carob Pod Nanoparticles: enhancing physicochemical, antioxidant, and antibacterial properties of innovative functional frozen yogurt.NPJ Sci Food. 2025 Jul 30;9(1):162. doi: 10.1038/s41538-025-00529-1. NPJ Sci Food. 2025. PMID: 40739151 Free PMC article.
-
Carob: A Mediterranean Resource for the Future.Plants (Basel). 2024 Apr 25;13(9):1188. doi: 10.3390/plants13091188. Plants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38732403 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Plant Taxa as Raw Material in Plant-Based Meat Analogues (PBMAs)-A Patent Survey.Nutrients. 2024 Nov 26;16(23):4054. doi: 10.3390/nu16234054. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 39683448 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alves MM, Antonov YuA, Gonçalves MP. The effect of structural features of gelatin on its thermodynamic compatibility with locust bean gum in aqueous media. Food Hydrocoll. 1999;13(2):157–166. doi: 10.1016/S0268-005X(98)00078-2. - DOI
-
- Aydinli M, Tutas M. Water sorption and water vapour permeability properties of polysaccharide (locust bean gum) based edible films. LWT Food Sci Technol. 2000;33(1):63–67. doi: 10.1006/fstl.1999.0617. - DOI
-
- Aydinol Sonmez P, Ozcan T. Assessment of structure and sensory characteristics of reduced fat yoghurt manufactured with carob bean gum polysaccharides. Food Sci Technol. 2021 doi: 10.1590/fst.61220. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
