Treatment of Basal Cell Carcinoma of the Lower Eyelid With High-Dose-Rate Brachytherapy
- PMID: 38410314
- PMCID: PMC10896607
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.53067
Treatment of Basal Cell Carcinoma of the Lower Eyelid With High-Dose-Rate Brachytherapy
Abstract
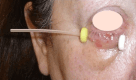
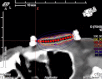
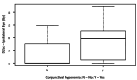
Objective To report the outcomes with high-dose-rate (HDR) brachytherapy (BT) treatment in patients with lower eyelid basal cell carcinoma (BCC) and to evaluate the relationship between dosimetric parameters and acute and late toxicities. Material and methods A retrospective unicentric study with patients diagnosed with lower eyelid biopsy-proven BCC treated with HDR BT between January 2012 and December 2019. The prescribed dose was 36 Gy to 40 Gy in 9 to 10 fractions, twice daily, over five days. The primary endpoint was local control, and the secondary endpoints were acute and late toxicities, registered according to CTCAE v4.0. The cosmetic result was evaluated on a qualitative scale (the CAIB scale). Local control was calculated according to the Kaplan-Meier test. Two sample T-tests and a Wilcoxon signed-rank test were used to determine the association between dosimetric parameters and side effects. Results Fifty-eight patients with a median age of 76 years were included. Among these patients, 55.2% received adjuvant HDR BT and 44.8% received radical HDR BT. At a median follow-up of 44 months, there were four local relapses, achieving a probability of local control at four years of 95% and 100% in the adjuvant and radical groups, respectively. Acute toxicity occurred in 76% of patients with only one grade 3 event (radiation dermatitis). Late toxicity was present in 56%. Eight patients underwent treatment for grade 3 cataracts during follow-up. Cosmetic results were excellent or very good in 93% of patients. Acute conjunctival hyperemia is strongly associated with the dose received by the ocular globe (volumes of 0.1cc, 1cc, and 2 cc) (p<0.05). Conclusion Lower eyelid BCC treatment with interstitial HDR BT is associated with excellent local control, acceptable long-term side effects, and good cosmetic results.
Keywords: basal cell carcinoma; eyelid; high-dose-rate brachytherapy; interstitial brachytherapy; skin cancer.
Copyright © 2024, Oliveira et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Interstitial high-dose-rate brachytherapy in eyelid cancer.Brachytherapy. 2015 Jul-Aug;14(4):554-64. doi: 10.1016/j.brachy.2015.03.005. Epub 2015 May 7. Brachytherapy. 2015. PMID: 25959364
-
Dosimetry of local failure with single dose 19 Gy high-dose-rate brachytherapy for prostate cancer.Radiother Oncol. 2021 Apr;157:93-98. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2021.01.006. Epub 2021 Jan 23. Radiother Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33493500
-
[HDR 192Ir brachytherapy in treatment of basal cell carcinoma of the lower eyelid and inner angle - our experience].Cesk Slov Oftalmol. 2013 Jun;69(2):75-9. Cesk Slov Oftalmol. 2013. PMID: 23964872 Czech.
-
Does an Algorithmic Approach to Using Brachytherapy and External Beam Radiation Result in Good Function, Local Control Rates, and Low Morbidity in Patients With Extremity Soft Tissue Sarcoma?Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2018 Mar;476(3):634-644. doi: 10.1007/s11999.0000000000000079. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2018. PMID: 29443850 Free PMC article.
-
Non-melanoma skin cancer treated with high-dose-rate brachytherapy: a review of literature.J Contemp Brachytherapy. 2016 Dec;8(6):533-540. doi: 10.5114/jcb.2016.64112. Epub 2016 Dec 2. J Contemp Brachytherapy. 2016. PMID: 28115960 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Interstitial brachytherapy for periocular nonmelanoma skin cancers: Impact on organ and function preservation.Tech Innov Patient Support Radiat Oncol. 2024 Oct 4;32:100280. doi: 10.1016/j.tipsro.2024.100280. eCollection 2024 Dec. Tech Innov Patient Support Radiat Oncol. 2024. PMID: 40161307 Free PMC article.
-
High-Dose-Rate Brachytherapy for Treatment of Facial Skin Cancers: Local Control, Toxicity, and Quality of Life in 67 Patients.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Aug 1;16(15):2742. doi: 10.3390/cancers16152742. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39123471 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Singh U, Kolavali RR. Surgical Ophthalmic Oncology. Springer International Publishing; 2019. Overview of Eyelid Tumors.
-
- Periocular basal cell carcinoma - current treatment concepts. Guo Y, Rokohl A, Kopecky A, et al. Ann Ey Sci. 2021;6:18.
-
- The GEC ESTRO handbook of brachytherapy. Martínez-Monge R, Guinot J, Haie-Meder C. https://user-swndwmf.cld.bz/10-General-Aspects-of-Head-and-Neck-Brachyth... ESTro. 2019
-
- GEC-ESTRO ACROP recommendations in skin brachytherapy. Guinot JL, Rembielak A, Perez-Calatayud J, et al. Radiother Oncol. 2018;126:377–385. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
