Laser-Assisted Surgical Management of Oral Mucocele: A Case Report
- PMID: 38410325
- PMCID: PMC10895208
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.53020
Laser-Assisted Surgical Management of Oral Mucocele: A Case Report
Abstract
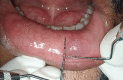
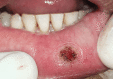
This case represents mucocele of extravasation phenomenon associated with a lower lip on the right side in the last 15 days. A 19-year-old male patient visited the outpatient department with a history of constant trauma due to lip biting and due to soft and flocculent consistency on palpation, mucocele was considered under the provisional diagnosis. The borders of the lesion were marked following all the protocols of asepsis and sterilization and laser-assisted surgical excision was undertaken resulting in total removal of the lesion with a diode laser by resecting it from the base to reduce chances of re-occurrence. The specimen that was resected was sent for histopathological examination, which confirmed the final diagnosis of mucous extravasation cyst or mucocele. The following report underlines that laser-assisted resection offers a minimally invasive and precision approach for the treatment of mucocele.
Keywords: diode laser; extravasation phenonmenon; histopath; mucocele; retention.
Copyright © 2024, Shinde et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Mucocele of the Lower Lip and Its Surgical Management.Cureus. 2024 Oct 5;16(10):e70874. doi: 10.7759/cureus.70874. eCollection 2024 Oct. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39497885 Free PMC article.
-
Mucous Extravasation Cyst Associated With the Lower Lip and Its Management: A Case Report.Cureus. 2023 Oct 5;15(10):e46557. doi: 10.7759/cureus.46557. eCollection 2023 Oct. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37933354 Free PMC article.
-
Oral mucocele: Review of literature and a case report.J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2015 Aug;7(Suppl 2):S731-3. doi: 10.4103/0975-7406.163516. J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2015. PMID: 26538955 Free PMC article.
-
Overview of the Clinical Benefits Using the Different Diode Laser Wavelengths in Treatment of the Mucocele: Clinical Cases Report Review.Photobiomodul Photomed Laser Surg. 2020 Aug;38(8):497-506. doi: 10.1089/photob.2019.4717. Photobiomodul Photomed Laser Surg. 2020. PMID: 32780688 Review.
-
Bilateral congenital mucous extravasation phenomenon: A rare case with literature review.J Indian Soc Pedod Prev Dent. 2018 Jan-Mar;36(1):93-96. doi: 10.4103/JISPPD.JISPPD_291_16. J Indian Soc Pedod Prev Dent. 2018. PMID: 29607847 Review.
Cited by
-
Mucocele of the Lower Lip and Its Surgical Management.Cureus. 2024 Oct 5;16(10):e70874. doi: 10.7759/cureus.70874. eCollection 2024 Oct. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39497885 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Oral mucocele: review of the literature. Ata-Ali J, Carrillo C, Bonet C, Balaguer J, Penarrocha M, Peñarrocha M. J Clin Exp Dent. 2010;2:18–21.
-
- Oral mucocele- a review. Kummar MA, Ebenezer V, Prakash D. https://www.proquest.com/docview/2799814457?sourcetype=Scholarly%20Journals J Pharm Sci Res. 2023;15:1060–1062.
-
- Mucocele of oral cavity: literature review and case report. Deshpande A, Lohe VK. https://www.jrmds.in/articles/mucocele-of-oral-cavity-literature-review-... J Res Med Dent Sci. 2022;10:51–53.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
