Run, walk, cheer or volunteer: a patient and public involvement survey
- PMID: 38410411
- PMCID: PMC10895219
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjsem-2023-001712
Run, walk, cheer or volunteer: a patient and public involvement survey
Abstract
Background: Children with chronic diseases have been reported to participate in less regular physical activity (PA) than peers without chronic diseases; and less than recommended in guidelines. Sheffield Children's Foundation Trust (SCFT) is an Active Hospitals pilot site, exploring options to facilitate PA for all children. One option is collaboration with Junior Parkrun: a free, weekly 2 km running event for children. The team investigated whether Junior Parkrun was of interest to guardians of children attending SCFT to increase PA.
Aims: This patient and public involvement survey assessed perceptions of PA for children attending SCFT according to their accompanying guardians. This will inform a possible collaboration between SCFT and Junior Parkrun.
Methods: A three-part, 14-question survey was developed, including demographics (age, ethnicity, postcode); perceptions of PA (barriers and facilitators); PA behaviours self-reported on Likert scales; and perceptions of Junior Parkrun. Guardians were asked whether they and their child would be interested in attending Junior Parkrun with SCFT staff support. This was distributed to guardians of children attending outpatient appointments.
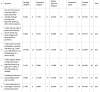
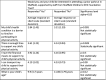
Results: 126 guardians responded. The average age of child was 10 years 10 months. 29.1% of guardians supported daily PA for their child. Almost half of respondents reported their child would be interested in attending Junior Parkrun. Of those not interested, the most common reason was travel.
Conclusion: The findings highlighted PA barriers perceived by guardians, and identified that almost half of respondents would be interested in attending Junior Parkrun. A collaboration between Junior Parkrun and SCFT could be explored.
Keywords: Adolescent; Children and exercise; Children's health and exercise; Exercise; Health promotion.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2024. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: Both AR and DR have previously participated in Parkrun but did not deliver the survey to participants to minimise influence.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Junior parkrun pilot in Australia: A real world evaluation.Health Promot J Austr. 2024 Jul;35(3):734-743. doi: 10.1002/hpja.812. Epub 2023 Sep 28. Health Promot J Austr. 2024. PMID: 37771130
-
Exploring the Health-Promoting Potential of the "parkrun" Phenomenon: What Factors are Associated With Higher Levels of Participation?Am J Health Promot. 2019 Jan;33(1):13-23. doi: 10.1177/0890117118770106. Epub 2018 Apr 23. Am J Health Promot. 2019. PMID: 29685052
-
Health and broader community benefit of parkrun-An exploratory qualitative study.Health Promot J Austr. 2019 Apr;30(2):163-171. doi: 10.1002/hpja.182. Epub 2018 Aug 5. Health Promot J Austr. 2019. PMID: 29939453
-
Parents' Perceptions of Children's and Adolescents' Use of Electronic Devices to Promote Physical Activity: Systematic Review of Qualitative Evidence.JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. 2023 Jul 20;11:e44753. doi: 10.2196/44753. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. 2023. PMID: 37471127 Free PMC article.
-
Outcomes of participation in parkrun, and factors influencing why and how often individuals participate: A systematic review of quantitative studies.J Sports Sci. 2022 Jul;40(13):1486-1499. doi: 10.1080/02640414.2022.2086522. Epub 2022 Jun 13. J Sports Sci. 2022. PMID: 35695484
References
-
- UK chief medical officers’ physical activity guidelines. 2019. Available: https://assets.publishing.service.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploa... [Accessed 10 Dec 2022].
-
- World Health Organization . Guidelines on physical activity, sedentary behaviour and sleep for children under 5 years of age. 2019. Available: https://iris.who.int/bitstream/handle/10665/311664/9789241550536-eng.pdf... [Accessed 01 Nov 2023]. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization . WHO guidelines on physical activity and sedentary behaviour. 2020. Available: https://iris.who.int/bitstream/handle/10665/336656/9789240015128-eng.pdf... [Accessed 01 Nov 2023]. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
