Clinical Efficacy and Mechanism of Vitamin D2 in Treating Hashimoto's Thyroiditis
- PMID: 38410421
- PMCID: PMC10896103
- DOI: 10.2147/JIR.S441120
Clinical Efficacy and Mechanism of Vitamin D2 in Treating Hashimoto's Thyroiditis
Abstract
Objective: Hashimoto's thyroiditis (HT) is one of the most common autoimmune diseases, with the highest incidence rate among autoimmune thyroid disorders. Vitamin D2 may have therapeutic effects on HT. This study aimed to elucidate the molecular mechanisms underlying vitamin D2 therapy for HT.
Methods: Differentially expressed genes (DEGs) associated with vitamin D2-treated HT were identified, and the DEG-associated gene enrichment pathway was explored using Gene Ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway enrichment analyses. The correlation between the hub genes and infiltrating immune cells was investigated, and the interactions among the hub genes and target drug and competing endogenous RNA (ceRNA; long non-coding RNA [lncRNA]-microRNA [miRNA]-messenger RNA [mRNA]) regulatory networks were determined.
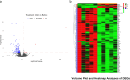
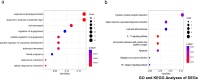
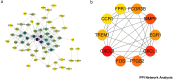
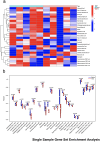
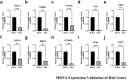
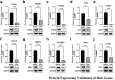
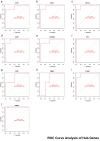
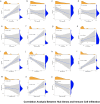
Results: GO and KEGG enrichment analyses identified a total of 102 DEGs (6 upregulated and 96 downregulated) in the vitamin D2-treated group samples. The area under the curve values of the identified 10 hub genes was as follows: CCR1(0.920), CXCL1 (0.960), CXCL8 (0.960), EGR1 (0.960), FCGR3B (0.920), FOS (1.000), FPR1 (0.840), MMP9 (0.720), PTGS2 (0.960), and TREM1 (1.000). The immune enrichment scores of the mast cell (P = 0.008), neutrophil (P = 0.016), and plasmacytoid dendritic cell (P = 0.016) were significantly decreased in the vitamin D2-treated group (P < 0.05). The hub gene/drug regulatory network included 8 hub genes, 108 molecular drugs, and 114 interaction relationship pairs. The ceRNA regulatory network included 129 lncRNAs, 145 miRNAs, mRNAs (hub genes), and 324 interaction relationship pairs.
Conclusion: Vitamin D2 may play an immunomodulatory role by regulating the aforementioned immune-related molecules and immune cells, thereby improving its therapeutic effects on HT.
Keywords: Hashimoto’s thyroiditis; RNA sequencing; differentially expressed genes; immune infiltration; vitamin D2.
© 2024 Gan and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests for this work.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Comprehensive analysis of hub biomarkers associated with immune and oxidative stress in Hashimoto's thyroiditis.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2023 Sep 1;745:109713. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2023.109713. Epub 2023 Aug 4. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2023. PMID: 37543352
-
Integrative Analyses of Genes Associated with Hashimoto's Thyroiditis.J Immunol Res. 2021 Aug 28;2021:8263829. doi: 10.1155/2021/8263829. eCollection 2021. J Immunol Res. 2021. PMID: 34493981 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive analysis of lncRNA-mediated ceRNA regulatory networks and key genes associated with papillary thyroid cancer coexistent with Hashimoto's thyroiditis.BMC Endocr Disord. 2022 Oct 20;22(1):252. doi: 10.1186/s12902-022-01173-6. BMC Endocr Disord. 2022. PMID: 36266640 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive analysis of an lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA competing endogenous RNA network in pulpitis.PeerJ. 2019 Jun 17;7:e7135. doi: 10.7717/peerj.7135. eCollection 2019. PeerJ. 2019. PMID: 31304055 Free PMC article.
-
Integrative analysis of the expression profiles of whole coding and non-coding RNA transcriptomes and construction of the competing endogenous RNA networks for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.Front Genet. 2023 Jan 30;14:1050783. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2023.1050783. eCollection 2023. Front Genet. 2023. PMID: 36793900 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

