This is a preprint.
CD40 Expression by B cells is Required for Optimal Immunity to Murine Pneumocystis Infection
- PMID: 38410485
- PMCID: PMC10896351
- DOI: 10.1101/2024.02.05.578900
CD40 Expression by B cells is Required for Optimal Immunity to Murine Pneumocystis Infection
Update in
-
CD40 Expression by B Cells Is Required for Optimal Immunity to Murine Pneumocystis Infection.J Infect Dis. 2024 Oct 16;230(4):1033-1041. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiae133. J Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 38478734 Free PMC article.
Abstract
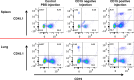
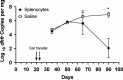
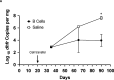
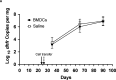
CD40-CD40L interactions are critical for controlling Pneumocystis infection. However, which CD40-expressing cell populations are important for this interaction have not been well-defined. We used a cohousing mouse model of Pneumocystis infection, combined with flow cytometry and qPCR, to examine the ability of different populations of cells from C57BL/6 mice to reconstitute immunity in CD40 knockout (KO) mice. Unfractionated splenocytes, as well as purified B cells, were able to control Pneumocystis infection, while B cell depleted splenocytes and unstimulated bone-marrow derived dendritic cells (BMDCs) were unable to control infection in CD40 KO mice. Pneumocystis antigen-pulsed BMDCs showed early, but limited, control of infection. Consistent with recent studies that have suggested a role for antigen presentation by B cells, using cells from immunized animals, B cells were able to present Pneumocystis antigens to induce proliferation of T cells. Thus, CD40 expression by B cells appears necessary for robust immunity to Pneumocystis.
Figures




Similar articles
-
CD40 Expression by B Cells Is Required for Optimal Immunity to Murine Pneumocystis Infection.J Infect Dis. 2024 Oct 16;230(4):1033-1041. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiae133. J Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 38478734 Free PMC article.
-
CD40 ligand is required for resolution of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia in mice.J Immunol. 1995 Oct 1;155(7):3525-9. J Immunol. 1995. PMID: 7561048
-
Immune responses to Pneumocystis murina are robust in healthy mice but largely absent in CD40 ligand-deficient mice.J Leukoc Biol. 2008 Aug;84(2):420-30. doi: 10.1189/jlb.1207816. Epub 2008 May 8. J Leukoc Biol. 2008. PMID: 18467653 Free PMC article.
-
The role of CD40 ligand in costimulation and T-cell activation.Immunol Rev. 1996 Oct;153:85-106. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1996.tb00921.x. Immunol Rev. 1996. PMID: 9010720 Review.
-
Functions of CD40 and its ligand, gp39 (CD40L).Crit Rev Immunol. 1996;16(1):59-108. doi: 10.1615/critrevimmunol.v16.i1.40. Crit Rev Immunol. 1996. PMID: 8809473 Review.
References
-
- Kovacs JA, Masur H. Evolving health effects of Pneumocystis: one hundred years of progress in diagnosis and treatment. JAMA 2009;301:2578–85 - PubMed
-
- Thomas CF Jr., Limper AH. Pneumocystis pneumonia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004;350:2487–98 - PubMed
-
- Levy J, Espanol-Boren T, Thomas C, et al. Clinical spectrum of X-linked hyper-IgM syndrome. J. Pediatr. 1997;131:47–54 - PubMed
-
- Martin SI, Fishman JA. Pneumocystis pneumonia in solid organ transplantation. Am. J. Transplant. 2013;13 Suppl 4:272–9 - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
