This is a preprint.
Targeting CCNE1 amplified ovarian and endometrial cancers by combined inhibition of PKMYT1 and ATR
- PMID: 38410486
- PMCID: PMC10896384
- DOI: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-3854682/v1
Targeting CCNE1 amplified ovarian and endometrial cancers by combined inhibition of PKMYT1 and ATR
Update in
-
Targeting CCNE1 amplified ovarian and endometrial cancers by combined inhibition of PKMYT1 and ATR.Nat Commun. 2025 Apr 1;16(1):3112. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-58183-w. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 40169546 Free PMC article.
Abstract
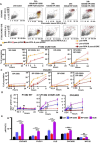
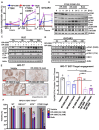
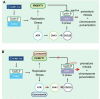
Ovarian cancers (OVCAs) and endometrial cancers (EMCAs) with CCNE1-amplification are often resistant to standard of care treatment and represent an unmet clinical need. Previously, synthetic-lethal screening identified loss of the CDK1 regulator, PKMYT1, as synthetically lethal with CCNE1-amplification. We hypothesized that CCNE1-amplification associated replication stress will be more effectively targeted by combining the PKMYT1 inhibitor, lunresertib (RP-6306), with the ATR inhibitor, camonsertib (RP-3500/RG6526). Low dose combination RP-6306 with RP-3500 synergistically increased cytotoxicity more in CCNE1 amplified compared to non-amplified cells. Combination treatment produced durable antitumor activity and increased survival in CCNE1 amplified patient-derived and cell line-derived xenografts. Mechanistically, low doses of RP-6306 with RP-3500 increase CDK1 activation more so than monotherapy, triggering rapid and robust induction of premature mitosis, DNA damage and apoptosis in a CCNE1-dependent manner. These findings suggest that targeting CDK1 activity by combining RP-6306 with RP-3500 is a novel therapeutic approach to treat CCNE1-amplifed OVCAs and EMCAs.
Keywords: ATR; CCNE1 amplification; PKMYT1.
Conflict of interest statement
Additional Declarations: Yes there is potential Competing Interest. F.S. serves on scientific advisory boards for AstraZeneca, GSK and Zentalis Pharmaceuticals. She has received institutional research funding from AstraZeneca, Repare Therapeutics, Instill Bio and Sierra Oncology.
Figures
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

