The human factor H protein family - an update
- PMID: 38410512
- PMCID: PMC10894998
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1135490
The human factor H protein family - an update
Abstract
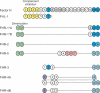
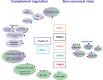
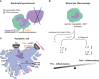
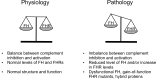
Complement is an ancient and complex network of the immune system and, as such, it plays vital physiological roles, but it is also involved in numerous pathological processes. The proper regulation of the complement system is important to allow its sufficient and targeted activity without deleterious side-effects. Factor H is a major complement regulator, and together with its splice variant factor H-like protein 1 and the five human factor H-related (FHR) proteins, they have been linked to various diseases. The role of factor H in inhibiting complement activation is well studied, but the function of the FHRs is less characterized. Current evidence supports the main role of the FHRs as enhancers of complement activation and opsonization, i.e., counter-balancing the inhibitory effect of factor H. FHRs emerge as soluble pattern recognition molecules and positive regulators of the complement system. In addition, factor H and some of the FHR proteins were shown to modulate the activity of immune cells, a non-canonical function outside the complement cascade. Recent efforts have intensified to study factor H and the FHRs and develop new tools for the distinction, quantification and functional characterization of members of this protein family. Here, we provide an update and overview on the versatile roles of factor H family proteins, what we know about their biological functions in healthy conditions and in diseases.
Keywords: Factor H; age-related macular degeneration; cancer; complement alternative pathway; factor H-related proteins; infection; inflammation; kidney disease.
Copyright © 2024 Sándor, Schneider, Matola, Barbai, Bencze, Hammad, Papp, Kövesdi, Uzonyi and Józsi.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Regulation of regulators: Role of the complement factor H-related proteins.Semin Immunol. 2019 Oct;45:101341. doi: 10.1016/j.smim.2019.101341. Epub 2019 Nov 19. Semin Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31757608 Review.
-
Factor H related proteins modulate complement activation on kidney cells.Kidney Int. 2022 Dec;102(6):1331-1344. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2022.07.035. Epub 2022 Sep 3. Kidney Int. 2022. PMID: 36063874 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction of the Factor H Family Proteins FHR-1 and FHR-5 With DNA and Dead Cells: Implications for the Regulation of Complement Activation and Opsonization.Front Immunol. 2020 Jul 16;11:1297. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01297. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32765490 Free PMC article.
-
Complement Factor H Family Proteins Modulate Monocyte and Neutrophil Granulocyte Functions.Front Immunol. 2021 Oct 4;12:660852. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.660852. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34671340 Free PMC article.
-
The Factor H protein family: The switchers of the complement alternative pathway.Immunol Rev. 2023 Jan;313(1):25-45. doi: 10.1111/imr.13166. Epub 2022 Nov 16. Immunol Rev. 2023. PMID: 36382387 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Chronic kidney disease enhances alternative pathway activity: a new paradigm.J Clin Invest. 2025 May 1;135(9):e188353. doi: 10.1172/JCI188353. eCollection 2025 May 1. J Clin Invest. 2025. PMID: 40309771 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Functional and structural characterization of mouse Factor H-related B protein unveils a novel dimerization domain shared by FHR-B and FH.Front Immunol. 2025 Jan 29;16:1522651. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1522651. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 39944688 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of human factor H-related gene and protein expressed in rheumatoid arthritis synovium identifies a novel mechanism promoting dysregulated complement pathway activation.Sci Rep. 2025 Jun 4;15(1):19633. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-03589-1. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40467630 Free PMC article.
-
Effective long-term treatment with moss-produced factor H by overcoming the antibody response in a mouse model of C3G.Front Immunol. 2025 Mar 7;16:1535547. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1535547. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40124383 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

