Clinical value of the red blood cell distribution width to albumin ratio in the assessment of prognosis in critically ill patients with sepsis: a retrospective analysis
- PMID: 38410549
- PMCID: PMC10894361
- DOI: 10.21037/jtd-23-1696
Clinical value of the red blood cell distribution width to albumin ratio in the assessment of prognosis in critically ill patients with sepsis: a retrospective analysis
Abstract
Background: Red blood cell (RBC) distribution width (RDW) to albumin ratio is a novel biomarker and its prognostic effect on critically ill patients with sepsis has not been extensively investigated. The objective of this study was to identify the prognostic value of the RDW to albumin ratio in these patients.
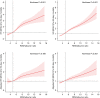
Methods: Data were extracted from the Medical Information Mart for Intensive Care III (MIMIC-III) database. A Cox proportional hazards model and restricted cubic spline model were used to determine the association of RDW to albumin ratio with mortality. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves and Kaplan-Meier survival curves were applied, and the area under the curve (AUC) was used to compare the predictive value.
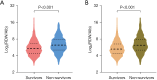
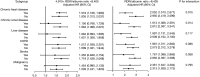
Results: A total of 3,969 eligible patients were enrolled. The median RDW to albumin ratio was significantly higher in non-survivors than in survivors at 30 and 90 days. Patients were divided into groups according to the RDW to albumin ratio, and the risk of 30- and 90-day mortality markedly increased in the group with a higher ratio. The relationship between the RDW to albumin ratio as a continuous variable and 30-day mortality also showed an upward trend in the restricted cubic spline. The AUC of the RDW to albumin ratio was 0.633 in discriminating 30-day mortality which was similar to that of the lactate to albumin ratio (AUC =0.617; P=0.133) and higher than that of the neutrophil percentage to albumin ratio (AUC =0.559; P<0.001).
Conclusions: The RDW to albumin ratio is a promising biomarker for assessing the prognosis of critically ill patients with sepsis. Its predictive value in determining mortality was found to be similar to that of the lactate to albumin ratio and superior to that of the neutrophil percentage to albumin ratio.
Keywords: Sepsis; albumin; prognosis; red blood cell distribution width (RDW).
2024 Journal of Thoracic Disease. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://jtd.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/jtd-23-1696/coif). C.J.W. reports fees for speaking and/or consulting from Biotest, CSL Behring, and Grifols. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Red blood cell distribution width predicts long-term mortality in critically ill patients with acute kidney injury: a retrospective database study.Sci Rep. 2020 Mar 12;10(1):4563. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-61516-y. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32165684 Free PMC article.
-
Red Blood Cell Distribution Width as a Predictor of 28-Day Mortality in Critically Ill Patients With Alcohol Use Disorder.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2020 Dec;44(12):2555-2560. doi: 10.1111/acer.14483. Epub 2020 Nov 16. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2020. PMID: 33067833 Free PMC article.
-
Association Between the Red Blood Cell Distribution Width and 30-Day Mortality in Intensive Care Patients Undergoing Cardiac Surgery: A Retrospective Observational Study Based on the Medical Information Mart for Intensive Care-IV Database.Ann Lab Med. 2024 Sep 1;44(5):401-409. doi: 10.3343/alm.2023.0345. Epub 2024 Mar 12. Ann Lab Med. 2024. PMID: 38469636 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Usefulness of Red Cell Distribution Width/Albumin Ratio to Discriminate 28-Day Mortality in Critically Ill Patients with Pneumonia Receiving Invasive Mechanical Ventilation, Compared with Lacate/Albumin Ratio: A Retrospective Cohort Study.Diagnostics (Basel). 2021 Dec 13;11(12):2344. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics11122344. Diagnostics (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34943582 Free PMC article.
-
A Meta-analysis of the Utility of Red Cell Distribution Width as a Biomarker to Predict Outcomes in Pediatric Illness (PROSPERO CRD42020208777).J Pediatr Intensive Care. 2021 Sep 15;13(4):307-314. doi: 10.1055/s-0041-1735876. eCollection 2024 Dec. J Pediatr Intensive Care. 2021. PMID: 39629347 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Association between red cell distribution width-to-albumin ratio and short-term mortality in patients with sepsis-associated delirium: a retrospective study from the MIMIC-IV database.BMC Anesthesiol. 2025 Apr 21;25(1):192. doi: 10.1186/s12871-025-03061-7. BMC Anesthesiol. 2025. PMID: 40259231 Free PMC article.
-
The red blood cell distribution width to albumin ratio was a potential prognostic biomarker for acute respiratory failure: a retrospective study.BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2024 Sep 13;24(1):253. doi: 10.1186/s12911-024-02639-4. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2024. PMID: 39272143 Free PMC article.
-
Association between red blood cell distribution width to albumin ratio (RAR) and long-term prognosis of patients with sudden cardiac arrest.J Thorac Dis. 2025 May 30;17(5):3032-3052. doi: 10.21037/jtd-2024-2030. Epub 2025 May 28. J Thorac Dis. 2025. PMID: 40529766 Free PMC article.
-
The Red Blood Cell Distribution Width to Albumin Ratio Is Associated with in Hospital Mortality and Adverse Outcome in Elderly Chinese Patients with Gastrointestinal Bleeding.J Inflamm Res. 2025 Apr 29;18:5811-5819. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S513844. eCollection 2025. J Inflamm Res. 2025. PMID: 40322531 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic value of red blood cell distribution width to albumin ratio for predicting mortality in adult patients meeting sepsis-3 criteria in intensive care units.BMC Anesthesiol. 2024 Jun 14;24(1):208. doi: 10.1186/s12871-024-02585-8. BMC Anesthesiol. 2024. PMID: 38877408 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
