Prognostic value of lactic dehydrogenase-to-albumin ratio in critically ill patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome: a retrospective cohort study
- PMID: 38410562
- PMCID: PMC10894402
- DOI: 10.21037/jtd-23-1238
Prognostic value of lactic dehydrogenase-to-albumin ratio in critically ill patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome: a retrospective cohort study
Abstract
Background: Lactic dehydrogenase (LDH)-to-albumin ratio (LAR) was an independent risk factor for mortality in the patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) due to coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), while the relationship among LAR and short-term, long-term, in-hospital mortalities of ARDS remains unclear. The current study aims to investigate the association between LAR and significant prognosis in patients with ARDS.
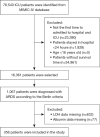
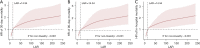
Methods: We conducted a retrospective cohort study and analyzed patients with ARDS on the Medical Information Mart for Intensive Care IV (MIMIC-IV) version 2.0 database. In the current study, 30-day mortality was defined as the primary outcome; 90-day mortality and in-hospital mortality were defined as secondary outcomes. Multivariate regression analysis, Kaplan-Meier curve analysis and subgroup analysis were performed to research the association between LAR and prognosis in patients with ARDS.
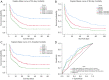
Results: A total of 358 critically ill patients with ARDS were enrolled in the current study. The mean age of the participants was 62.6±16.0 and the median of LAR was 14.3. According to the Kaplan-Meier curve analysis, the higher LAR group had a higher 30-day, 90-day and in-hospital mortalities. We also analyzed the 30-day mortality to receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves by comparing the value between LAR and LAR + simplified acute physiology score II (SAPS II). The area under the curve (AUC) of the LAR group was 0.694 [95% confidence interval (CI): 0.634-0.754, P<0.001], and 0.661 for the LAR + SAPS II (95% CI: 0.599-0.722, P<0.001). For 30-day mortality, after adjusting for covariates, hazard ratios (HRs) (95% CIs) for tertile 2 (LAR 8.7-30.9) and tertile 3 (LAR >30.9) were 2.00 (1.37, 2.92) and 2.50 (1.50, 4.15), respectively. Similar results were also observed for 90-day mortality and in-hospital mortality.
Conclusions: Elevated LAR levels are associated with increased 30- and 90-day mortalities, as well as in-hospital mortality in patients with ARDS, which means LAR levels may predict the mortalities of ARDS patients.
Keywords: Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS); intensive care unit (ICU); lactic dehydrogenase-to-albumin ratio (LAR); mortality; prognosis.
2024 Journal of Thoracic Disease. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://jtd.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/jtd-23-1238/coif). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Association between lactate-to-albumin ratio and short-time mortality in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome.J Clin Anesth. 2024 Dec;99:111632. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinane.2024.111632. Epub 2024 Sep 26. J Clin Anesth. 2024. PMID: 39326299
-
The association between lactate dehydrogenase to serum albumin ratio and the 28-day mortality in patients with sepsis-associated acute kidney injury in intensive care: a retrospective cohort study.Ren Fail. 2023 Dec;45(1):2212080. doi: 10.1080/0886022X.2023.2212080. Ren Fail. 2023. PMID: 37194715 Free PMC article.
-
Association between lactate-to-albumin ratio and mortality in hepatic failure: a retrospective cohort study.BMC Infect Dis. 2025 Mar 28;25(1):433. doi: 10.1186/s12879-025-10783-z. BMC Infect Dis. 2025. PMID: 40155840 Free PMC article.
-
The Lactate/Albumin Ratio Predicts Mortality in Critically Ill Patients with Acute Kidney Injury: An Observational Multicenter Study on the eICU Database.Int J Gen Med. 2021 Dec 30;14:10511-10525. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S339767. eCollection 2021. Int J Gen Med. 2021. PMID: 35002307 Free PMC article.
-
Lactate-to-Albumin Ratio (LAR) as a Predictor of All-Cause Mortality in Patients With Myocardial Infarction: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Cureus. 2025 Apr 13;17(4):e82166. doi: 10.7759/cureus.82166. eCollection 2025 Apr. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40364881 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Association between the lactate dehydrogenase-to-albumin ratio and 28-day mortality in septic patients with malignancies: analysis of the MIMIC-IV database.BMC Cancer. 2025 Apr 8;25(1):637. doi: 10.1186/s12885-025-14013-2. BMC Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40200294 Free PMC article.
-
Association between lactate dehydrogenase and 28-day all-cause mortality in patients with non-traumatic intracerebral hemorrhage: A retrospective analysisof the MIMIC-IV database.Biomol Biomed. 2025 Jan 30;25(3):663-671. doi: 10.17305/bb.2024.11189. Biomol Biomed. 2025. PMID: 39508803 Free PMC article.
-
Association Between Lactic Dehydrogenase-to-Albumin Ratio and Short-Time Mortality in Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease.Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2025 Jul 15;20:2435-2444. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S521192. eCollection 2025. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2025. PMID: 40688237 Free PMC article.
-
Association between lactate dehydrogenase to albumin ratio and ICU mortality in patients with acute kidney injury: a retrospective cohort study.Front Nephrol. 2025 Jun 2;5:1583913. doi: 10.3389/fneph.2025.1583913. eCollection 2025. Front Nephrol. 2025. PMID: 40530353 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluating Mortality Predictors in COVID-19 Intensive Care Unit Patients: Insights into Age, Procalcitonin, Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio, Platelet-to-Lymphocyte Ratio, and Ferritin Lactate Index.Diagnostics (Basel). 2024 Mar 24;14(7):684. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics14070684. Diagnostics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38611597 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Saguil A, Fargo MV. Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome: Diagnosis and Management. Am Fam Physician 2020;101:730-8. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
