Surgical lung biopsy for suspected interstitial lung disease with video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery is safe, providing exact histological and disease specific diagnosis for tailoring treatment
- PMID: 38410568
- PMCID: PMC10894428
- DOI: 10.21037/jtd-23-1107
Surgical lung biopsy for suspected interstitial lung disease with video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery is safe, providing exact histological and disease specific diagnosis for tailoring treatment
Abstract
Background: Surgical lung biopsy (SLB) is required for diagnosis in patients with suspected interstitial lung disease (ILD) if other less invasive diagnostic methods are non-conclusive. We evaluated the outcome of SLB by using centralized databases in a whole-nation patient-cohort.
Methods: A population-based retrospective study on 68 consecutive patients (mean age 58 years, 58.8% males) that underwent SLB in Iceland between the years 2008 and 2020. Patient information was obtained from patient charts and peri- and postoperative complications were registered together with 30- and 90-day mortality. Computed tomography (CT) scans, histological biopsies and spirometry results were reviewed, and overall survival (Kaplan-Meier) estimated. Mean follow-up was 61.3 months (range, 3-155 months).
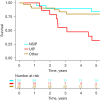
Results: Out of 68 SLB-patients 41 (60.3%) had preoperatively undergone non-conclusive transbronchial biopsies (TBB) obtained with bronchoscopy. Spirometry showed forced vital capacity (FVC) 3.0 L and forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1) 2.3 L, or 73.0% and 71.6% of predicted value, respectively. Video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery (VATS) technique was used in all cases and provided a histologic and disease specific diagnosis in 92.6% of cases; most often being nonspecific interstitial pneumonia (NSIP) (29.4%) and usual interstitial pneumonia (UIP) (23.5%). One patient (1.5%) sustained a major postoperative complication (excessive bleeding) and seven patients (10.3%) minor complications. Median chest tube time and length of stay was 1 and 2 days, respectively. No patients died <90 days postoperatively. Overall survival at 1 and 5 years was 95.6% and 73.5%, respectively, and 5-year survival for NSIP and UIP was 85% and 43.7%, respectively. Long-term mortality for UIP was four times higher when compared with NSIP and other diagnosis.
Conclusions: Lung biopsy with VATS-technique provided a definitive histological and disease specific diagnosis in majority of cases. The procedure is safe, reflected in low complication-rates and short hospital stay, and can therefore be used to diagnose and tailor treatment of ILD patients.
Keywords: 30-day mortality; Interstitial lung disease (ILD); histology; surgical biopsy; video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery (VATS).
2024 Journal of Thoracic Disease. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://jtd.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/jtd-23-1107/coif). G.G. reports funding from the Landspitali Scientific Fund (No. A2020-019) and the University of Iceland Research Fund. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
