Taxonomic and functional shifts of gut microbiome in immunoglobulin A vasculitis children and their mothers
- PMID: 38410769
- PMCID: PMC10895042
- DOI: 10.3389/fped.2024.1356529
Taxonomic and functional shifts of gut microbiome in immunoglobulin A vasculitis children and their mothers
Abstract
Objectives: To examine the gut microbiota characteristics in children with immunoglobulin A vasculitis and their interrelationships with the host, while evaluate the vertical inheritance of microbiota in the development and progression of IgA vasculitis.
Methods: This study investigated the gut microbiome of 127 IgA vasculitis mother-child pairs and 62 matched healthy mother-child pairs, and compared the gut microbial composition of different groups. The pathway enrichment analysis evaluated potential gut microbiome-mediated pathways involved in the pathophysiology of IgA vasculitis. The Spearman correlation analysis illustrated the relationships between clinical variables and bacterial biomarkers.
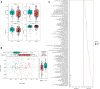
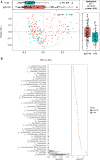
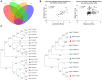
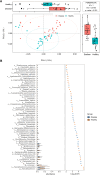
Results: This study identified distinct intestinal microbiome in IgA vasculitis children compared to healthy children, and further pointed out the association in gut microbiota between IgA vasculitis children's and their mother's. The relative abundance of Megamonas and Lactobacillus in IgAV children was positively correlated with that in their mothers. The pathway enrichment analysis found microbial biosynthesis of vitamins and essential amino acids was upregulated in children with IgA vasculitis. Correlation analysis showed bacterial biomarkers were correlated with indicators of blood coagulation.
Conclusion: Children with IgA vasculitis have unique bacterial biomarkers and may affect coagulation function, and their gut microbiome was closely associated with that of their mothers. The observed association in gut microbiota between IgA vasculitis children and their mothers suggested a potential intergenerational influence of the maternal microbiota on the development or progression of IgA vasculitis in children.
Keywords: bacterial biomarker; gut microbiota; immunoglobulin A vasculitis; microbial pathway; mother-child pairs.
© 2024 Liang, Zhao, Zhao, Sheng, Chen, Zhao, Wang and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Differential gut microbiota and inflammatory cytokines contribute to IgA vasculitis.Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2025 Apr;43(4):563-574. doi: 10.55563/clinexprheumatol/ff61t7. Epub 2025 Apr 8. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2025. PMID: 40201970
-
Metagenomic profiling reveals dominance of gram-positive bacteria in the gut microbiome shifts associated with immunoglobulin A vasculitis (Henoch-Schönlein Purpura).Clin Transl Immunology. 2021 Oct 8;10(10):e1342. doi: 10.1002/cti2.1342. eCollection 2021. Clin Transl Immunology. 2021. PMID: 34646556 Free PMC article.
-
Correlation of Gut Microbiome Between ASD Children and Mothers and Potential Biomarkers for Risk Assessment.Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 2019 Feb;17(1):26-38. doi: 10.1016/j.gpb.2019.01.002. Epub 2019 Apr 23. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 2019. PMID: 31026579 Free PMC article.
-
Gut Microbes in Immunoglobulin A Nephropathy and Their Potential Therapeutic Applications.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 May 17;9:823267. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.823267. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35655857 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Drug-induced IgA vasculitis in children and adults: Revisiting drug causality using a dual pharmacovigilance-based approach.Autoimmun Rev. 2021 Jan;20(1):102707. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2020.102707. Epub 2020 Nov 14. Autoimmun Rev. 2021. PMID: 33197572 Review.
Cited by
-
Unravelling the Link between the Gut Microbiome and Autoimmune Kidney Diseases: A Potential New Therapeutic Approach.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Apr 28;25(9):4817. doi: 10.3390/ijms25094817. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38732038 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

