NLRP1 restricts porcine deltacoronavirus infection via IL-11 inhibiting the phosphorylation of the ERK signaling pathway
- PMID: 38411106
- PMCID: PMC10949457
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.01982-23
NLRP1 restricts porcine deltacoronavirus infection via IL-11 inhibiting the phosphorylation of the ERK signaling pathway
Abstract
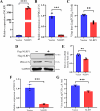
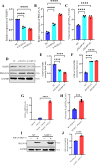
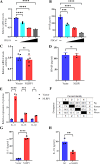
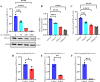
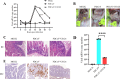
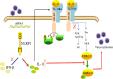
Continuously emerging highly pathogenic coronaviruses remain a major threat to human and animal health. Porcine deltacoronavirus (PDCoV) is a newly emerging enterotropic swine coronavirus that causes large-scale outbreaks of severe diarrhea disease in piglets. Unlike other porcine coronaviruses, PDCoV has a wide range of species tissue tropism, including primary human cells, which poses a significant risk of cross-species transmission. Nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-like receptor (NLR) family pyrin domain-containing 1 (NLRP1) has a key role in linking host innate immunity to microbes and the regulation of inflammatory pathways. We now report a role for NLRP1 in the control of PDCoV infection. Overexpression of NLRP1 remarkably suppressed PDCoV infection, whereas knockout of NLRP1 led to a significant increase in PDCoV replication. A mechanistic study revealed that NLRP1 suppressed PDCoV replication in cells by upregulating IL-11 expression, which in turn inhibited the phosphorylation of the ERK signaling pathway. Furthermore, the ERK phosphorylation inhibitor U0126 effectively hindered PDCoV replication in pigs. Together, our results demonstrated that NLRP1 exerted an anti-PDCoV effect by IL-11-mediated inhibition of the phosphorylation of the ERK signaling pathway, providing a novel antiviral signal axis of NLRP1-IL-11-ERK. This study expands our understanding of the regulatory network of NLRP1 in the host defense against virus infection and provides a new insight into the treatment of coronaviruses and the development of corresponding drugs.IMPORTANCECoronavirus, which mainly infects gastrointestinal and respiratory epithelial cells in vivo, poses a huge threat to both humans and animals. Although porcine deltacoronavirus (PDCoV) is known to primarily cause fatal diarrhea in piglets, reports detected in plasma samples from Haitian children emphasize the potential risk of animal-to-human spillover. Finding effective therapeutics against coronaviruses is crucial for controlling viral infection. Nucleotide-binding oligomerization-like receptor (NLR) family pyrin domain-containing 1 (NLRP1), a key regulatory factor in the innate immune system, is highly expressed in epithelial cells and associated with the pathogenesis of viruses. We demonstrate here that NLRP1 inhibits the infection of the intestinal coronavirus PDCoV through IL-11-mediated phosphorylation inhibition of the ERK signaling pathway. Furthermore, the ERK phosphorylation inhibitor can control the infection of PDCoV in pigs. Our study emphasizes the importance of NLRP1 as an immune regulatory factor and may open up new avenues for the treatment of coronavirus infection.
Keywords: ERK signaling; anti-coronavirus; interleukin-11; nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-like receptor family pyrin domain-containing 1; porcine deltacoronavirus.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Porcine deltacoronavirus nucleocapsid protein antagonizes JAK-STAT signaling pathway by targeting STAT1 through KPNA2 degradation.J Virol. 2024 Jul 23;98(7):e0033424. doi: 10.1128/jvi.00334-24. Epub 2024 Jun 3. J Virol. 2024. PMID: 38829137 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide CRISPR/Cas9 Screen Reveals a Role for SLC35A1 in the Adsorption of Porcine Deltacoronavirus.J Virol. 2022 Dec 21;96(24):e0162622. doi: 10.1128/jvi.01626-22. Epub 2022 Dec 1. J Virol. 2022. PMID: 36453883 Free PMC article.
-
25-Hydroxycholesterol Mediates Cholesterol Metabolism to Restrict Porcine Deltacoronavirus Infection via Suppression of Transforming Growth Factor β1.Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Dec 21;10(6):e0219822. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.02198-22. Epub 2022 Oct 31. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 36314946 Free PMC article.
-
Epidemiology, pathogenesis, immune evasion mechanism and vaccine development of porcine Deltacoronavirus.Funct Integr Genomics. 2024 Apr 24;24(3):79. doi: 10.1007/s10142-024-01346-7. Funct Integr Genomics. 2024. PMID: 38653845 Review.
-
Porcine deltacoronavirus infection: Etiology, cell culture for virus isolation and propagation, molecular epidemiology and pathogenesis.Virus Res. 2016 Dec 2;226:50-59. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2016.04.009. Epub 2016 Apr 13. Virus Res. 2016. PMID: 27086031 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Dong BQ, Liu W, Fan XH, Vijaykrishna D, Tang XC, Gao F, Li LF, Li GJ, Zhang JX, Yang LQ, Poon LLM, Zhang SY, Peiris JSM, Smith GJD, Chen H, Guan Y. 2007. Detection of a novel and highly divergent coronavirus from Asian leopard cats and Chinese ferret badgers in Southern China. J Virol 81:6920–6926. doi:10.1128/JVI.00299-07 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Woo PCY, Lau SKP, Lam CSF, Lau CCY, Tsang AKL, Lau JHN, Bai R, Teng JLL, Tsang CCC, Wang M, Zheng B-J, Chan K-H, Yuen K-Y. 2012. Discovery of seven novel mammalian and avian coronaviruses in the genus deltacoronavirus supports bat coronaviruses as the gene source of alphacoronavirus and betacoronavirus and avian coronaviruses as the gene source of gammacoronavirus and deltacoronavirus. J Virol 86:3995–4008. doi:10.1128/JVI.06540-11 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

