Intranasal Epitope-Polymer Vaccine Lodges Resident Memory T Cells Protecting Against Influenza Virus
- PMID: 38411375
- PMCID: PMC11469178
- DOI: 10.1002/adhm.202304188
Intranasal Epitope-Polymer Vaccine Lodges Resident Memory T Cells Protecting Against Influenza Virus
Abstract
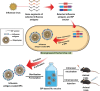
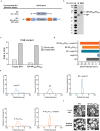
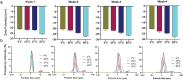
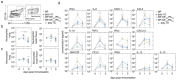
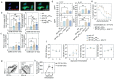
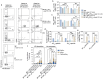
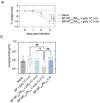
Intranasal vaccines, unlike injectable vaccines, boost immunity along the respiratory tract; this can significantly limit respiratory virus replication and shedding. There remains a need to develop mucosal adjuvants and vaccine delivery systems that are both safe and effective following intranasal administration. Here, biopolymer particles (BP) densely coated with repeats of MHC class I restricted immunodominant epitopes derived from influenza A virus namely NP366, a nucleoprotein-derived epitope and PA224, a polymerase acidic subunit derived epitope, are bioengineered. These BP-NP366/PA224 can be manufactured at a high yield and are obtained at ≈93% purity, exhibiting ambient-temperature stability. Immunological characterization includes comparing systemic and mucosal immune responses mounted following intramuscular or intranasal immunization. Immunization with BP-NP366/PA224 without adjuvant triggers influenza-specific CD8+ T cell priming and memory CD8+ T cell development. Co-delivery with the adjuvant poly(I:C) significantly boosts the size and functionality of the influenza-specific pulmonary resident memory CD8+ T cell pool. Intranasal, but not intramuscular delivery of BP-NP366/PA224 with poly(I:C), provides protection against influenza virus challenge. Overall, the BP approach demonstrates as a suitable antigen formulation for intranasal delivery toward induction of systemic protective T cell responses against influenza virus.
Keywords: influenza; intranasal delivery; polyhydroxybutyrate; resident memory T cells; subunit vaccine; vaccine.
© 2024 The Authors. Advanced Healthcare Materials published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
B.H.A.R. is a cofounder and shareholder of PolyBatics Ltd.
Figures

References
-
- Wakim L. M., Smith J., Caminschi I., Lahoud M. H., Villadangos J. A., Mucosal Immunol. 2015, 8, 1060. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

