Circadian Rhythm Regulation by Pacemaker Neuron Chloride Oscillation in Flies
- PMID: 38411570
- PMCID: PMC11368518
- DOI: 10.1152/physiol.00006.2024
Circadian Rhythm Regulation by Pacemaker Neuron Chloride Oscillation in Flies
Abstract
Circadian rhythms in physiology and behavior sync organisms to external environmental cycles. Here, circadian oscillation in intracellular chloride in central pacemaker neurons of the fly, Drosophila melanogaster, is reviewed. Intracellular chloride links SLC12 cation-coupled chloride transporter function with kinase signaling and the regulation of inwardly rectifying potassium channels.
Keywords: SLC12; SPAK; WNK; circadian; potassium channel.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflicts of interest, financial or otherwise, are declared by the author.
Figures
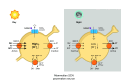
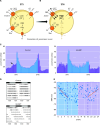
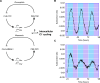
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

