The value of periportal hyperintensity sign from gadobenate dimeglumine-enhanced hepatobiliary phase MRI for predicting clinical outcomes in patients with decompensated cirrhosis
- PMID: 38411746
- PMCID: PMC10899122
- DOI: 10.1186/s13244-024-01629-4
The value of periportal hyperintensity sign from gadobenate dimeglumine-enhanced hepatobiliary phase MRI for predicting clinical outcomes in patients with decompensated cirrhosis
Erratum in
-
Correction: The value of periportal hyperintensity sign from gadobenate dimeglumine-enhanced hepatobiliary phase MRI for predicting clinical outcomes in patients with decompensated cirrhosis.Insights Imaging. 2024 May 12;15(1):117. doi: 10.1186/s13244-024-01706-8. Insights Imaging. 2024. PMID: 38735022 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Objectives: To determine the value of periportal hyperintensity sign from gadobenate dimeglumine (Gd-BOPTA)-enhanced hepatobiliary phase (HBP) magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) for predicting clinical outcomes in patients with decompensated cirrhosis.
Methods: A total of 199 cirrhotic patients who underwent Gd-BOPTA-enhanced MRI were divided into control group (n = 56) and decompensated cirrhosis group (n = 143). The presence of periportal hyperintensity sign on HBP MRI was recorded. The Cox regression model was used to investigate the association between periportal hyperintensity sign and clinical outcomes.
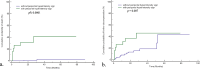
Results: There was a significant difference in the frequency of periportal hyperintensity sign on HBP between compensated and decompensated cirrhotic patients (p < 0.05). After a median follow-up of 29.0 months (range, 1.0-90.0 months), nine out of 143 patients (6.2%) with decompensated cirrhosis died. Periportal hyperintensity sign on HBP MRI was a significant risk factor for death (hazard ratio (HR) = 23.677; 95% confidence interval (CI) = 4.759-117.788; p = 0.0001), with an area under the curve (AUC) of 0.844 (95% CI = 0.774-0.899). Thirty patients (20.9%) developed further decompensation. Periportal hyperintensity sign on HBP MRI was also a significant risk factor for further decompensation (HR = 2.594; 95% CI = 1.140-5.903; p = 0.023).
Conclusions: Periportal hyperintensity sign from Gd-BOPTA-enhanced HBP MRI is valuable for predicting clinical outcomes in patients with decompensated cirrhosis.
Critical relevance statement: Periportal hyperintensity sign from gadobenate dimeglumine-enhanced hepatobiliary phase magnetic resonance imaging is a new noninvasive method to predict clinical outcomes in patients with decompensated cirrhosis.
Key points: • There was a significant difference in the frequency of periportal hyperintensity sign on HBP between compensated and decompensated cirrhotic patients. • Periportal hyperintensity sign on the hepatobiliary phase was a significant risk factor for death in patients with decompensated cirrhosis. • Periportal hyperintensity sign on the hepatobiliary phase was a significant risk factor for further decompensation in patients with decompensated cirrhosis.
Keywords: Gadobenate dimeglumine, Periportal hyperintensity sign, Liver cirrhosis, Magnetic resonance imaging, Clinical outcomes.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- European Association for the Study of the Liver Electronic address: easloffice@easloffice.eu; European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines for the management of patients with decompensated cirrhosis. J Hepatol. 2018;69(2):406–460. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2018.03.024. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

