Outcomes of fenestrated endovascular abdominal aortic repair in distal entry tears of chronic debakey IIIb aortic dissection
- PMID: 38412141
- PMCID: PMC10898741
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0288218
Outcomes of fenestrated endovascular abdominal aortic repair in distal entry tears of chronic debakey IIIb aortic dissection
Abstract
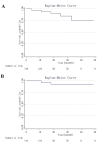
Currently, there have been very few reports within the literature which specifically address using fenestrated and branched stent grafts to completely isolate and repair distal entry tears of chronic DeBakey IIIb aortic dissection. This study aimed to evaluate the clinical outcomes of a 3-dimensional (3D) printed aortic model-guided fenestrated stent in the treatment of distal tears of chronic DeBakey IIIb aortic dissection after thoracic endovascular aortic repair (TEVAR). The study was a one-center retrospective study comprising 36 patients who underwent TEVAR and fenestrated endovascular abdominal aortic repair (F-EVAR) between April 2014 and December 2022. Patient data was compiled and analysed for preoperative, intraoperative, and perioperative characteristics. In total, 36 patients (12 females and 24 males) were incorporated into this study. All of the patients included in this study had hypertension, and among them, the leading cause for undergoing II-stage F-EVAR was the progression of a false lumen, accounting for 24 cases (66.7% of the total). The technical success rate was 97.2% and there were no cases of 30-day mortality, myocardial infarction, permanent paraparesis, or organ failure. One year post-F-EVAR treatment, surviving patients showed significant false and true lumen remodelling with 100% complete false-lumen thrombosis. A total of five patients died during the follow-up, two patients died related to aorta complications and three patients died of heart failure, multiple organ failure, or septic shock. II-stage F-EVAR was safe and feasible operation to repair all distal tears of chronic DeBakey IIIb aortic dissection.
Copyright: © 2024 Cui et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Thoracic endovascular aortic repair for chronic DeBakey IIIb aortic dissection.Ann Thorac Surg. 2014 Dec;98(6):2092-7; discussion 2098. doi: 10.1016/j.athoracsur.2014.06.066. Epub 2014 Oct 1. Ann Thorac Surg. 2014. PMID: 25282168 Free PMC article.
-
Endovascular treatment of chronic aortic dissection with fenestrated and branched stent grafts.J Vasc Surg. 2021 May;73(5):1573-1582.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2020.10.004. Epub 2020 Oct 15. J Vasc Surg. 2021. PMID: 33068767
-
Aortic remodeling after false lumen occlusion using an atrial septal occluder in chronic DeBakey IIIb aortic dissection.J Vasc Surg. 2022 Jun;75(6):1864-1871.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2021.12.060. Epub 2022 Jan 5. J Vasc Surg. 2022. PMID: 34995720
-
Clinical and Morphologic Outcomes of Endovascular Repair for Subacute and Chronic Type B Aortic Dissection.Ann Vasc Surg. 2021 Apr;72:390-399. doi: 10.1016/j.avsg.2020.08.107. Epub 2020 Sep 2. Ann Vasc Surg. 2021. PMID: 32889157
-
Fate and Consequences of the False Lumen After Thoracic Endovascular Aortic Repair in Type B Aortic Dissection.Ann Vasc Surg. 2023 Aug;94:32-37. doi: 10.1016/j.avsg.2022.09.042. Epub 2022 Oct 26. Ann Vasc Surg. 2023. PMID: 36309167 Review.
References
-
- Erbel R, Aboyans V, Boileau C, Bossone E, Di Bartolomeo R, Eggebrecht H, et al.: [2014 ESC Guidelines on the diagnosis and treatment of aortic diseases]. Kardiol Pol 2014, 72(12):1169–1252. - PubMed
-
- Riambau V, Bockler D, Brunkwall J, Cao P, Chiesa R, Coppi G, et al.: Editor’s Choice—Management of Descending Thoracic Aorta Diseases: Clinical Practice Guidelines of the European Society for Vascular Surgery (ESVS). Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg 2017, 53(1):4–52. doi: 10.1016/j.ejvs.2016.06.005 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

