SLC20A1 is a prospective prognostic and therapy response predictive biomarker in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
- PMID: 38412319
- PMCID: PMC10968711
- DOI: 10.18632/aging.205597
SLC20A1 is a prospective prognostic and therapy response predictive biomarker in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
Abstract
Background: SLC20A1, a prominent biomarker in several cancers, has been understudied in its predictive role in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC).
Methods: The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) database was used to analyze HNSCC prognosis, SLC20A1 overexpression, and clinical characteristics. Quantitative real-time PCR and Western blot analysis confirmed SLC20A1 expression in HNSCC tissues. Cellular behaviors such as invasion, migration and proliferation were assessed using Transwell, wound healing and colony formation assays. Immune system data were obtained from the Tumor Immune Estimation Resource (TIMER) and CIBERSORT databases. Gene Ontology (GO), Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG), and Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (GSEA) were used to explore biological parameters and pathways associated with SLC20A1 overexpression in HNSCC.
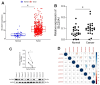
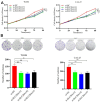
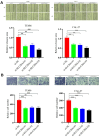
Results: In 499 HNSCC samples, SLC20A1 mRNA and protein expression were significantly higher than in 44 normal counterparts, confirmed by 24 paired samples. Patients were categorized based on SLC20A1 levels, survival status and overall survival. High SLC20A1 expression correlated with advanced T stage, increased risk scores and decreased survival. Stage, age and SLC20A1 expression emerged as independent predictive factors for HNSCC in univariate and multivariate analyses. SLC20A1 overexpression, which is associated with poor prognosis, may influence cell proliferation, migration, invasion, chemotherapy response, and the immune milieu.
Conclusions: SLC20A1 overexpression in HNSCC, characterized by increased cellular invasion, migration and proliferation, is a potential prognostic biomarker and therapeutic response indicator.
Keywords: SLC20A1; TCGA; cancer; prognosis; squamous cell carcinoma.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

