Integrative omics analysis elucidates the genetic basis underlying seed weight and oil content in soybean
- PMID: 38412459
- PMCID: PMC11132872
- DOI: 10.1093/plcell/koae062
Integrative omics analysis elucidates the genetic basis underlying seed weight and oil content in soybean
Abstract
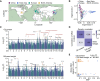
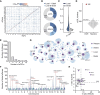
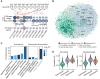
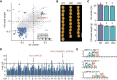
Synergistic optimization of key agronomic traits by traditional breeding has dramatically enhanced crop productivity in the past decades. However, the genetic basis underlying coordinated regulation of yield- and quality-related traits remains poorly understood. Here, we dissected the genetic architectures of seed weight and oil content by combining genome-wide association studies (GWAS) and transcriptome-wide association studies (TWAS) using 421 soybean (Glycine max) accessions. We identified 26 and 33 genetic loci significantly associated with seed weight and oil content by GWAS, respectively, and detected 5,276 expression quantitative trait loci (eQTLs) regulating expression of 3,347 genes based on population transcriptomes. Interestingly, a gene module (IC79), regulated by two eQTL hotspots, exhibited significant correlation with both seed weigh and oil content. Twenty-two candidate causal genes for seed traits were further prioritized by TWAS, including Regulator of Weight and Oil of Seed 1 (GmRWOS1), which encodes a sodium pump protein. GmRWOS1 was verified to pleiotropically regulate seed weight and oil content by gene knockout and overexpression. Notably, allelic variations of GmRWOS1 were strongly selected during domestication of soybean. This study uncovers the genetic basis and network underlying regulation of seed weight and oil content in soybean and provides a valuable resource for improving soybean yield and quality by molecular breeding.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of American Society of Plant Biologists.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement. None declared.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Natural allelic variation in SW14 determines seed weight and quality in soybean.Nat Commun. 2025 Aug 29;16(1):8070. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-63582-0. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 40877292 Free PMC article.
-
Soybean genome‑wide association study of seed weight, protein, and oil content in the southeastern USA.Mol Genet Genomics. 2025 Apr 12;300(1):43. doi: 10.1007/s00438-025-02228-8. Mol Genet Genomics. 2025. PMID: 40220041 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide Association and RNA-Seq Analyses Reveal a Potential Candidate Gene Related to Oil Content in Soybean Seeds.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 25;25(15):8134. doi: 10.3390/ijms25158134. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39125702 Free PMC article.
-
Integration of omics approaches to understand oil/protein content during seed development in oilseed crops.Plant Cell Rep. 2017 May;36(5):637-652. doi: 10.1007/s00299-016-2064-1. Epub 2016 Oct 27. Plant Cell Rep. 2017. PMID: 27796489 Review.
-
Understanding the Molecular Regulatory Networks of Seed Size in Soybean.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jan 24;25(3):1441. doi: 10.3390/ijms25031441. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38338719 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Genome and transcriptome wide association study identify candidate genes regulating folate levels in maize.Front Plant Sci. 2025 Jun 19;16:1606220. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2025.1606220. eCollection 2025. Front Plant Sci. 2025. PMID: 40612597 Free PMC article.
-
Tiny seeds, big decisions: Jasmonate-mediated regulation of seed size in Arabidopsis via the SOD7-KLU module.Plant Cell. 2025 Jul 1;37(7):koaf160. doi: 10.1093/plcell/koaf160. Plant Cell. 2025. PMID: 40515682 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
GPS: Harnessing data fusion strategies to improve the accuracy of machine learning-based genomic and phenotypic selection.Plant Commun. 2025 Aug 11;6(8):101416. doi: 10.1016/j.xplc.2025.101416. Epub 2025 Jun 11. Plant Commun. 2025. PMID: 40509592 Free PMC article.
-
Editorial: Omics in seed development: challenges and opportunities for improving of seed quality and yield in model and crop plants.Front Plant Sci. 2025 Feb 20;16:1568039. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2025.1568039. eCollection 2025. Front Plant Sci. 2025. PMID: 40051876 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
A system genetics analysis uncovers the regulatory variants controlling drought response in wheat.Plant Biotechnol J. 2025 May;23(5):1565-1584. doi: 10.1111/pbi.14605. Epub 2025 Feb 20. Plant Biotechnol J. 2025. PMID: 39977251 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bastian M, Heymann S, Jacomy M. Gephi: an open source software for exploring and manipulating networks. Proc Int AAAI Conf Web Soc Media. 2009:3(1):361–362. 10.1609/icwsm.v3i1.13937 - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

