The highly selective and oral phosphoinositide 3-kinase delta (PI3K-δ) inhibitor roginolisib induces apoptosis in mesothelioma cells and increases immune effector cell composition
- PMID: 38412661
- PMCID: PMC10907864
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tranon.2023.101857
The highly selective and oral phosphoinositide 3-kinase delta (PI3K-δ) inhibitor roginolisib induces apoptosis in mesothelioma cells and increases immune effector cell composition
Abstract
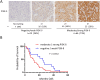
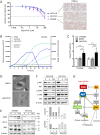
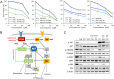
Targeting aberrantly expressed kinases in malignant pleural mesothelioma (MPM) is a promising therapeutic strategy. We here investigated the effect of the novel and highly selective Phosphoinositide 3-kinase delta (PI3K-δ) inhibitor roginolisib (IOA-244) on MPM cells and on the immune cells in MPM microenvironment. To this aim, we analyzed the expression of PI3K-δ by immunohistochemistry in specimens from primary MPM, cell viability and death in three different MPM cell lines treated with roginolisib alone and in combination with ipatasertib (AKT inhibitor) and sapanisertib (mTOR inhibitor). In a co-culture model of patient-derived MPM cells, autologous peripheral blood mononuclear cells and fibroblasts, the tumor cell viability and changes in immune cell composition were investigated after treatment of roginolisib with nivolumab and cisplatin. PI3K-δ was detected in 66/89 (74%) MPM tumors and was associated with reduced overall survival (12 vs. 25 months, P=0.0452). Roginolisib induced apoptosis in MPM cells and enhanced the anti-tumor efficacy of AKT and mTOR kinase inhibitors by suppressing PI3K-δ/AKT/mTOR and ERK1/2 signaling. Furthermore, the combination of roginolisib with chemotherapy and immunotherapy re-balanced the immune cell composition, increasing effector T-cells and reducing immune suppressive cells. Overall, roginolisib induces apoptosis in MPM cells and increases the antitumor immune cell effector function when combined with nivolumab and cisplatin. These results provide first insights on the potential of roginolisib as a therapeutic agent in patients with MPM and its potential in combination with established immunotherapy regimen.
Keywords: PI3/AKT/mTOR inhibition; Phosphoinositide 3-kinase delta (PI3K-δ); apoptosis; combinatorial therapy; malignant pleural mesothelioma; tumor induced-immunosuppression.
Copyright © 2024. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare the following financial interests/personal relationships which may be considered as potential competing interests: Claudia Kalla, German Ott and Roger Falkenstern-Ge received Roginolisib from iOnctura SA and grants from iOnctura SA, Charles River Germany GmbH and Robert Bosch Stiftung (grant project 704 to CK, GO and RG-G); Francesca Finotello received grants from iOnctura SA; Karolina Niewola-Staszkowska, Giusy di Conza, Michael Lahn and Lars van der Veen are employees of iOnctura SA; Michael Lahn and Lars van der Veen are the stock owner of Roginolisib; Julia Schueler received funding from Charles River Germany GmbH; Joanna Kopecka received funding from Fondazione Cassa di Rispoarmio di Torino (grant 2021); Chiara Riganti received Roginolisib from iOnctura SA and grants from from iOnctura SA, and Italian Association for Cancer Research (IG 21480).
Figures



Similar articles
-
Non-Clinical Toxicology Evaluation of the Novel Non-ATP Competitive Oral PI3 Kinase Delta Inhibitor Roginolisib.Int J Toxicol. 2023 Dec;42(6):515-534. doi: 10.1177/10915818231200419. Epub 2023 Sep 4. Int J Toxicol. 2023. PMID: 37667445 Free PMC article.
-
PI3 Kinase Pathway and MET Inhibition is Efficacious in Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma.Sci Rep. 2016 Sep 13;6:32992. doi: 10.1038/srep32992. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27623107 Free PMC article.
-
MET and PI3K/mTOR as a potential combinatorial therapeutic target in malignant pleural mesothelioma.PLoS One. 2014 Sep 15;9(9):e105919. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0105919. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25221930 Free PMC article.
-
[Systemic Treatment of Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma].Gan To Kagaku Ryoho. 2017 Dec;44(13):2041-2047. Gan To Kagaku Ryoho. 2017. PMID: 29361614 Review. Japanese.
-
Progress in the Understanding of the Immune Microenvironment and Immunotherapy in Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma.Curr Drug Targets. 2020;21(15):1606-1612. doi: 10.2174/1389450121666200719011234. Curr Drug Targets. 2020. PMID: 32682370 Review.
Cited by
-
Epitranscriptomic RNA m6A Modification in Cancer Therapy Resistance: Challenges and Unrealized Opportunities.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024 Dec 11;12(4):e2403936. doi: 10.1002/advs.202403936. Online ahead of print. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024. PMID: 39661414 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of PI3k-Gamma Modulation in Bacterial Infection: A Review of the Literature and Selected Experimental Observations.Antibiotics (Basel). 2025 Mar 18;14(3):315. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics14030315. Antibiotics (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40149125 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Signaling pathways in liver cancer: pathogenesis and targeted therapy.Mol Biomed. 2024 May 31;5(1):20. doi: 10.1186/s43556-024-00184-0. Mol Biomed. 2024. PMID: 38816668 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeted Therapy in Mesotheliomas: Uphill All the Way.Cancers (Basel). 2024 May 22;16(11):1971. doi: 10.3390/cancers16111971. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38893092 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bueno R., Stawiski E.W., Goldstein L.D., Durinck S., De Rienzo A., Modrusan Z., Gnad F., Nguyen T.T., Jaiswal B.S., Chirieac L.R., Sciaranghella D., Dao N., Gustafson C.E., Munir K.J., Hackney J.A., Chaudhuri A., Gupta R., Guillory J., Toy K., Ha C., Chen Y.J., Stinson J., Chaudhuri S., Zhang N., Wu T.D., Sugarbaker D.J., de Sauvage F.J., Richards W.G., Seshagiri S. Comprehensive genomic analysis of malignant pleural mesothelioma identifies recurrent mutations, gene fusions and splicing alterations. Nat. Genet. 2016;48(4):407–416. - PubMed
-
- Baas P., Scherpereel A., Nowak A.K., Fujimoto N., Peters S., Tsao A.S., Mansfield A.S., Popat S., Jahan T., Antonia S., Oulkhouir Y., Bautista Y., Cornelissen R., Greillier L., Grossi F., Kowalski D., Rodriguez-Cid J., Aanur P., Oukessou A., Baudelet C., Zalcman G. First-line nivolumab plus ipilimumab in unresectable malignant pleural mesothelioma (CheckMate 743): a multicentre, randomised, open-label phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2021;397(10272):375–386. - PubMed
-
- Peters S., Scherpereel A., Cornelissen R., Oulkhouir Y., Greillier L., Kaplan M.A., Talbot T., Monnet I., Hiret S., Baas P., Nowak A.K., Fujimoto N., Tsao A.S., Mansfield A.S., Popat S., Zhang X., Hu N., Balli D., Spires T., Zalcman G. First-line nivolumab plus ipilimumab versus chemotherapy in patients with unresectable malignant pleural mesothelioma: 3-year outcomes from CheckMate 743. Ann. Oncol. 2022;33(5):488–499. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

