The economic impact of international travel measures used during the COVID-19 pandemic: a scoping review
- PMID: 38413100
- PMCID: PMC10900439
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjgh-2023-013900
The economic impact of international travel measures used during the COVID-19 pandemic: a scoping review
Abstract
Introduction: Assessment of the use of travel measures during COVID-19 has focused on their effectiveness in achieving public health objectives. However, the prolonged use of highly varied and frequently changing measures by governments, and their unintended consequences caused, has been controversial. This has led to a call for coordinated decision-making focused on risk-based approaches, which requires better understanding of the broader impacts of international travel measures (ITMs) on individuals and societies.
Methods: Our scoping review investigates the literature on the economic impact of COVID-19 ITMs. We searched health, social science and COVID-19-specific databases for empirical studies preprinted or published between 1 January 2020 and 31 October 2023. Evidence was charted using a narrative approach and included jurisdiction of study, ITMs studied, study design, outcome categories, and main findings.
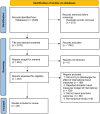
Results: Twenty-six studies met the inclusion criteria and were included for data extraction. Twelve of them focused on the international travel restrictions implemented in early 2020. Limited attention was given to measures such as entry/exit screening and vaccination requirements. Eight studies focused on high-income countries, 6 on low-income and middle-income countries and 10 studies were comparative although did not select countries by income. Economic outcomes assessed included financial markets (n=13), economic growth (n=4), economic activities (n=1), performance of industries central to international travel (n=9), household-level economic status (n=3) and consumer behaviour (n=1). Empirical methods employed included linear regression (n=17), mathematical modelling (n=3) and mixed strategies (n=6).
Conclusion: Existing studies have begun to provide evidence of the wide-ranging economic impacts resulting from ITMs. However, the small body of research combined with difficulties in isolating the effects of such measures and limitations in available data mean that it is challenging to draw general and robust conclusions. Future research using rigorous empirical methods and high-quality data is needed on this topic.
Keywords: COVID-19; health economics; systematic review.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2024. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Understanding the secondary outcomes of international travel measures during the covid-19 pandemic: a scoping review of social impact evidence.Global Health. 2024 Aug 1;20(1):59. doi: 10.1186/s12992-024-01064-6. Global Health. 2024. PMID: 39090727 Free PMC article.
-
Unintended health and societal consequences of international travel measures during the COVID-19 pandemic: a scoping review.J Travel Med. 2021 Oct 11;28(7):taab123. doi: 10.1093/jtm/taab123. J Travel Med. 2021. PMID: 34369562 Free PMC article.
-
Travel-related control measures to contain the COVID-19 pandemic: a rapid review.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Oct 5;10:CD013717. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013717. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Mar 25;3:CD013717. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013717.pub2. PMID: 33502002 Updated.
-
International travel-related control measures to contain the COVID-19 pandemic: a rapid review.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Mar 25;3(3):CD013717. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013717.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 33763851 Free PMC article.
-
Unintended consequences of measures implemented in the school setting to contain the COVID-19 pandemic: a scoping review.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Jun 6;6(6):CD015397. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015397. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024 Dec 12;12:CD015397. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015397.pub2. PMID: 35661990 Free PMC article. Updated.
Cited by
-
Understanding the secondary outcomes of international travel measures during the covid-19 pandemic: a scoping review of social impact evidence.Global Health. 2024 Aug 1;20(1):59. doi: 10.1186/s12992-024-01064-6. Global Health. 2024. PMID: 39090727 Free PMC article.
-
Latest revisions to the International Health Regulations will fail to prevent future travel chaos.BMJ Glob Health. 2025 Jan 29;10(1):e017077. doi: 10.1136/bmjgh-2024-017077. BMJ Glob Health. 2025. PMID: 39880415 Free PMC article.
-
Understanding macroeconomic indicators affected by COVID-19 containment policies in the United States: a scoping review.Health Aff Sch. 2025 Mar 6;3(4):qxaf045. doi: 10.1093/haschl/qxaf045. eCollection 2025 Apr. Health Aff Sch. 2025. PMID: 40190702 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The adoption of international travel measures during the first year of the COVID-19 pandemic: a descriptive analysis.Global Health. 2024 Oct 4;20(1):72. doi: 10.1186/s12992-024-01071-7. Global Health. 2024. PMID: 39367505 Free PMC article.
-
Observational Study on the Clinical Reality of Community-Acquired Respiratory Virus Infections in Adults and Older Individuals.Pathogens. 2024 Nov 9;13(11):983. doi: 10.3390/pathogens13110983. Pathogens. 2024. PMID: 39599536 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous