Extrasynaptic localization is essential for α5GABAA receptor modulation of dopamine system function
- PMID: 38413199
- PMCID: PMC10972738
- DOI: 10.1523/ENEURO.0344-23.2023
Extrasynaptic localization is essential for α5GABAA receptor modulation of dopamine system function
Abstract
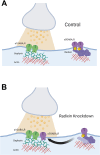
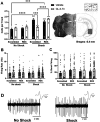
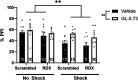
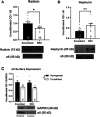
Dopamine system dysfunction, observed in animal models with psychosis-like symptomatology, can be restored by targeting Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid type A receptors (GABAAR) containing the α5, but not α1, subunit in the ventral hippocampus (vHipp). The reason for this discrepancy in efficacy remains elusive; however, one key difference is that α1GABAARs are primarily located in the synapse, whereas α5GABAARs are mostly extrasynaptic. To test whether receptor location is responsible for this difference in efficacy, we injected a small interfering ribonucleic acid (siRNA) into the vHipp to knock down radixin, a scaffolding protein that holds α5GABAARs in the extrasynaptic space. We then administered GL-II-73, a positive allosteric modulator of α5GABAARs (α5-PAM) known to reverse shock-induced deficits in dopamine system function, to determine if shifting α5GABAARs from the extrasynaptic space to the synapse would prevent the effects of α5-PAM on dopamine system function. As expected, knockdown of radixin significantly decreased radixin-associated α5GABAARs and increased the proportion of synaptic α5GABAARs, without changing the overall expression of α5GABAARs. Importantly, GL-II-73 was no longer able to modulate dopamine neuron activity in radixin-knockdown rats, indicating that the extrasynaptic localization of α5GABAARs is critical for hippocampal modulation of the dopamine system. These results may have important implications for clinical use of GL-II-73, as periods of high hippocampal activity appear to favor synaptic α5GABAARs, thus efficacy may be diminished in conditions where aberrant hippocampal activity is present.Significance Statement Currently available treatments for psychosis, a debilitating symptom linked with several brain disorders, are inadequate. While they can help manage symptoms in some patients, they do so imperfectly. They are also associated with severe side effects that can cause discontinuation of medication. This study provides preclinical evidence that the drug, GL-II-73, possesses the ability to modulate dopamine activity, a key player in psychosis symptoms, and further provides some mechanistic details regarding these effects. Overall, this work contributes to the growing body of literature suggesting that GL-II-73 and similar compounds may possess antipsychotic efficacy.
Copyright © 2024 McCoy et al.
Figures
Update of
-
Extrasynaptic localization is essential for α5GABA A receptor modulation of dopamine system function.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Jul 14:2023.07.12.548744. doi: 10.1101/2023.07.12.548744. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: eNeuro. 2024 Feb 27:ENEURO.0344-23.2023. doi: 10.1523/ENEURO.0344-23.2023. PMID: 37502875 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Bakshi VP, Alsene KM, Roseboom PH, Connors EE (2012) Enduring sensorimotor gating abnormalities following predator exposure or corticotropin-releasing factor in rats: a model for PTSD-like information-processing deficits? Neuropharmacology 62:737–748. 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2011.01.040 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Boudreau AC, Milovanovic M, Conrad KL, Nelson C, Ferrario CR, Wolf ME (2012) A protein cross-linking assay for measuring cell surface expression of glutamate receptor subunits in the rodent brain after in vivo treatments. Curr Protoc Neurosci Chapter 5:Unit 5.30.1-19. 10.1002/0471142301.ns0530s59 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
