Biological study of skin wound treated with Alginate/Carboxymethyl cellulose/chorion membrane, diopside nanoparticles, and Botox A
- PMID: 38413625
- PMCID: PMC10899239
- DOI: 10.1038/s41536-024-00354-2
Biological study of skin wound treated with Alginate/Carboxymethyl cellulose/chorion membrane, diopside nanoparticles, and Botox A
Abstract
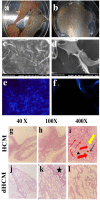
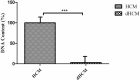
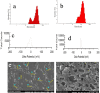
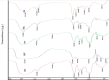
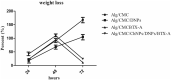
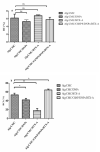
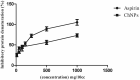
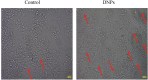
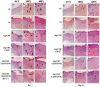
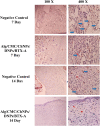
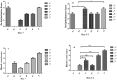
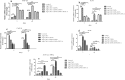
A hydrogel-based wound dressing with desirable properties is necessary for achieving functional skin integrity post-injury. This study focuses on preparing a hydrogel using Alginate/Carboxymethyl cellulose (Alg/CMC) as a base material. To evaluate its regenerative effects on full-thickness wounds, diopside nanoparticles and Botulinum toxin A (BTX-A) were incorporated into the hydrogel along with chorion membrane. The diopside nanoparticles (DNPs) act as a proangiogenic factor, promoting proliferation and regulating inflammation, while the chorion membrane facilitates these processes. Additionally, BTX-A prevents scar formation and aids in wound closure. The nanoparticles and hydrogel were characterized using various techniques, and their cytocompatibility was assessed. In vivo studies and quantitative polymerase chain reaction analysis showed that wound area reduction was significant after two weeks of treatment with the Alg/CMC/ChNPs/DNPs/BTX-A hydrogel. Overall, this scaffold demonstrated potential for promoting tissue regeneration and new epithelization formation, making it a promising candidate for enhancing skin restoration in wound treatments.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Biological macromolecules Alginate-Carboxymethyl Cellulose (Alg-CMC) hydrogel loaded with Botulinum toxin type A for skin wound treatment and functional tissue regeneration.Int J Biol Macromol. 2025 Jun;316(Pt 2):144668. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2025.144668. Epub 2025 May 26. Int J Biol Macromol. 2025. PMID: 40436176
-
Enhancing pressure ulcer healing and tissue regeneration by using N-acetyl-cysteine loaded carboxymethyl cellulose/gelatin/sodium alginate hydrogel.Biomed Eng Lett. 2024 Apr 20;14(4):833-845. doi: 10.1007/s13534-024-00378-z. eCollection 2024 Jul. Biomed Eng Lett. 2024. PMID: 38946815 Free PMC article.
-
On-Demand Dissolvable Self-Healing Hydrogel Based on Carboxymethyl Chitosan and Cellulose Nanocrystal for Deep Partial Thickness Burn Wound Healing.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2018 Dec 5;10(48):41076-41088. doi: 10.1021/acsami.8b14526. Epub 2018 Nov 16. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2018. PMID: 30398062
-
A novel multifunctional chitosan-gelatin/carboxymethyl cellulose-alginate bilayer hydrogel containing human placenta extract for accelerating full-thickness wound healing.Int J Biol Macromol. 2023 Dec 31;253(Pt 3):126929. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.126929. Epub 2023 Sep 17. Int J Biol Macromol. 2023. PMID: 37717877
-
Exploring the recent developments of alginate silk fibroin material for hydrogel wound dressing: A review.Int J Biol Macromol. 2023 Sep 1;248:125989. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.125989. Epub 2023 Jul 25. Int J Biol Macromol. 2023. PMID: 37499726 Review.
Cited by
-
Alginate-Based Hydrogels with Amniotic Membrane Stem Cells for Wound Dressing Application.Stem Cells Cloning. 2025 Jan 10;18:1-13. doi: 10.2147/SCCAA.S493125. eCollection 2025. Stem Cells Cloning. 2025. PMID: 39816853 Free PMC article.
-
Innovative hydrogels in cutaneous wound healing: current status and future perspectives.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2025 May 12;13:1454903. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2025.1454903. eCollection 2025. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 40421113 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intradermal Injection of Hybrid Complexes of High- and Low-Molecular-Weight Hyaluronan: Where Do We Stand and Where Are We Headed in Regenerative Medicine?Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Mar 12;25(6):3216. doi: 10.3390/ijms25063216. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38542191 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regeneration of the skin wound by two different crosslinkers: In vitro and in vivo studies.Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2025;28(2):194-208. doi: 10.22038/ijbms.2024.80137.17361. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2025. PMID: 39850117 Free PMC article.
-
Silk Fibroin Microparticle/Carboxymethyl Cellulose Composite Gel for Wound Healing Applications.Biomimetics (Basel). 2025 Jul 2;10(7):434. doi: 10.3390/biomimetics10070434. Biomimetics (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40710247 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Schreml S, et al. The impact of the pH value on skin integrity and cutaneous wound healing. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2010;24:373–378. - PubMed
-
- Khazaei, M., Alizadeh, M. & Rezakhani, L. Resveratrol‐loaded decellularized ovine pericardium: ECM introduced for tissue engineering. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. (2023). - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

