Association of tissue oxygen saturation levels with skeletal muscle injury in the critically ill
- PMID: 38413660
- PMCID: PMC10899231
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-55118-1
Association of tissue oxygen saturation levels with skeletal muscle injury in the critically ill
Abstract
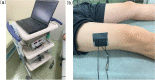
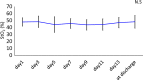
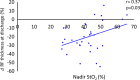
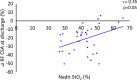
This study aimed to investigate the association between the level of tissue oxygen saturation (StO2) and quadriceps/skeletal muscle dysfunction, measured using the Medical Research Council (MRC) scale and ultrasonography, in critically ill patients. Thirty-four patients hospitalized at the Critical Care Medicine Center of Kindai University Hospital, between January 2022 and March 2023, were enrolled in this study. The StO2 of the quadriceps muscle was measured via near-infrared spectroscopy. Muscle atrophy was measured by the thickness, cross-sectional area (CSA), and echo intensity of the rectus femoris (RF). These values were evaluated every alternate day until 13 days after admission or until discharge, whichever occurred first. Muscle weakness was assessed using the sum score of the MRC scale (MRC-SS), with the patient sitting at bedside. The mean age of the patients was 67.3 ± 15.3 years, and 20 (59%) were men. Seven patients (21%) were admitted for trauma, and 27 (79%) were admitted for medical emergencies or others. The mean score for the MRC-SS was 51.0 ± 7.9 points. RF thickness and CSA significantly decreased after day 7 (p < 0.05). There were no significant changes in StO2 levels during hospitalization. However, there were positive correlations between the nadir StO2 during hospitalization and MRC-SS, and changes in RF thickness and CSA at discharge (r = 0.41, p = 0.03; r = 0.37, p = 0.03; and r = 0.35, p = 0.05, respectively). StO2 in the quadriceps muscle may be useful for predicting muscle atrophy and dysfunction in patients with critical illnesses.
Keywords: Cross-sectional area; Medical Research Council (MRC) scale; Near-infrared spectroscopy; Rectus femoris; Tissue oxygen saturation; Ultrasonography.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
[Clinical value of early bedside ultrasound measurement of quadriceps femoris in diagnosis of ICU-acquired weakness].Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2020 Jul 7;100(25):1967-1972. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112137-20191129-02609. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2020. PMID: 32629598 Chinese.
-
Quantitative peripheral muscle ultrasound in sepsis: Muscle area superior to thickness.J Crit Care. 2018 Oct;47:324-330. doi: 10.1016/j.jcrc.2018.04.003. J Crit Care. 2018. PMID: 30224027 Free PMC article.
-
[Dynamic changes of diaphragm and limb skeletal muscle in patients with sepsis assessed by bedside ultrasound and their correlation with blood urea/creatinine ratio].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2024 Jun;36(6):643-648. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20230803-00577. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2024. PMID: 38991965 Chinese.
-
Skeletal Muscle Ultrasonography in Nutrition and Functional Outcome Assessment of Critically Ill Children: Experience and Insights From Pediatric Disease and Adult Critical Care Studies [Formula: see text].JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 2017 Sep;41(7):1091-1099. doi: 10.1177/0148607116683143. Epub 2016 Dec 1. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 2017. PMID: 29049016 Review.
-
Skeletal muscle oxygen saturation (StO2) measured by near-infrared spectroscopy in the critically ill patients.Biomed Res Int. 2013;2013:502194. doi: 10.1155/2013/502194. Epub 2013 Aug 21. Biomed Res Int. 2013. PMID: 24027757 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

