Protective effect of microbisporicin (NAI-107) against vancomycin resistant Enterococcus faecium infection in a Galleria mellonella model
- PMID: 38413672
- PMCID: PMC10899196
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-55262-8
Protective effect of microbisporicin (NAI-107) against vancomycin resistant Enterococcus faecium infection in a Galleria mellonella model
Abstract
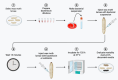
Increasing antimicrobial resistance in Enterococcus faecium necessitates the search for novel treatment agents, such as bacteriocins. In this study, we conducted an in vivo assessment of five bacteriocins, namely Lacticin Z, Lacticin Q, Garvicin KS (ABC), Aureocin A53 and Microbisporicin (NAI-107), against vanB-resistant Enterococcus faecium using a Galleria mellonella model. Our in vitro experiments demonstrated the efficacy of all five bacteriocins against vanB-resistant E. faecium with only NAI-107 demonstrating in vivo efficacy. Notably, NAI-107 exhibited efficacy across a range of tested doses, with the highest efficacy observed at a concentration of 16 µg/mL. Mortality rates in the group treated with 16 µg/mL NAI-107 were lower than those observed in the linezolid-treated group. These findings strongly suggest that NAI-107 holds promise as a potential alternative therapeutic agent for treating infections caused by resistant E. faecium and warrants further investigation.
Keywords: Enterococcus faecium; Galleria mellonella; Lantibiotics; Microbisporicin; NAI-107; VanB.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Hidron AI, et al. Antimicrobial-resistant pathogens associated with healthcare-associated infections: Annual summary of data reported to the National Healthcare Safety Network at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 2006–2007. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2008;29(11):996–1011. doi: 10.1086/591861. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

