Drinkable in situ-forming tough hydrogels for gastrointestinal therapeutics
- PMID: 38413810
- PMCID: PMC11364503
- DOI: 10.1038/s41563-024-01811-5
Drinkable in situ-forming tough hydrogels for gastrointestinal therapeutics
Abstract
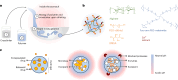
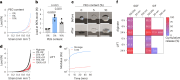
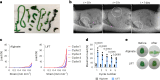
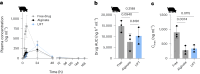
Pills are a cornerstone of medicine but can be challenging to swallow. While liquid formulations are easier to ingest, they lack the capacity to localize therapeutics with excipients nor act as controlled release devices. Here we describe drug formulations based on liquid in situ-forming tough (LIFT) hydrogels that bridge the advantages of solid and liquid dosage forms. LIFT hydrogels form directly in the stomach through sequential ingestion of a crosslinker solution of calcium and dithiol crosslinkers, followed by a drug-containing polymer solution of alginate and four-arm poly(ethylene glycol)-maleimide. We show that LIFT hydrogels robustly form in the stomachs of live rats and pigs, and are mechanically tough, biocompatible and safely cleared after 24 h. LIFT hydrogels deliver a total drug dose comparable to unencapsulated drug in a controlled manner, and protect encapsulated therapeutic enzymes and bacteria from gastric acid-mediated deactivation. Overall, LIFT hydrogels may expand access to advanced therapeutics for patients with difficulty swallowing.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
G.W.L., M.J.P., R.L. and G.T. are co-inventors on patent application PCT/US2023/076701 (filed 12 October 2023), which describes the system reported here. Complete details of all relationships for-profit and not for-profit for G.T. can be found in Supplementary Table 3. Complete details for R.L. can be found in Supplementary Table 4. M.J. consults for VitaKey. All other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
In Situ Forming, Cytocompatible, and Self-Recoverable Tough Hydrogels Based on Dual Ionic and Click Cross-Linked Alginate.Biomacromolecules. 2018 May 14;19(5):1646-1662. doi: 10.1021/acs.biomac.8b00140. Epub 2018 Apr 10. Biomacromolecules. 2018. PMID: 29596739
-
3D Printing of Highly Stretchable and Tough Hydrogels into Complex, Cellularized Structures.Adv Mater. 2015 Jul 15;27(27):4035-40. doi: 10.1002/adma.201501099. Epub 2015 Jun 1. Adv Mater. 2015. PMID: 26033288 Free PMC article.
-
Facile Synthesis of Highly Stretchable, Tough, and Photodegradable Hydrogels.Adv Healthc Mater. 2023 Sep;12(22):e2300918. doi: 10.1002/adhm.202300918. Epub 2023 May 15. Adv Healthc Mater. 2023. PMID: 37133868
-
Refined control of thermoresponsive swelling/deswelling and drug release properties of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) hydrogels using hydrophilic polymer crosslinkers.J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2016 Dec;27(17):1698-1711. doi: 10.1080/09205063.2016.1230933. Epub 2016 Sep 11. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2016. PMID: 27573586
-
Polyethylene glycol (PEG)-Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) (PNIPAAm) based thermosensitive injectable hydrogels for biomedical applications.Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2014 Nov;88(3):575-85. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2014.07.005. Epub 2014 Aug 1. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2014. PMID: 25092423 Review.
Cited by
-
Retrievable hydrogel networks with confined microalgae for efficient antibiotic degradation and enhanced stress tolerance.Nat Commun. 2025 Apr 2;16(1):3160. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-58415-z. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 40175365 Free PMC article.
-
Diverse reactivity of maleimides in polymer science and beyond.Polym Int. 2025 Apr;74(4):296-306. doi: 10.1002/pi.6715. Epub 2024 Nov 5. Polym Int. 2025. PMID: 40255264
-
Oral olsalazine/ellagic acid/ZnCl2-modified in situ-forming hydrogels alleviates anxiety/depression-like symptoms and brain neural activity in colitis mice.Mater Today Bio. 2025 Jul 8;33:102058. doi: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2025.102058. eCollection 2025 Aug. Mater Today Bio. 2025. PMID: 40688678 Free PMC article.
-
Oral microbiota-regulating and inflammation-targeted polymersome-hydrogels for RNAi therapy of ulcerative colitis.Bioact Mater. 2025 Jul 4;53:32-44. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2025.06.039. eCollection 2025 Nov. Bioact Mater. 2025. PMID: 40688025 Free PMC article.
-
Porous Hydrogels Prepared by Two-Step Gelation Method for Bone Regeneration.J Funct Biomater. 2025 Mar 13;16(3):100. doi: 10.3390/jfb16030100. J Funct Biomater. 2025. PMID: 40137379 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

