Role of lung ornithine aminotransferase in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: regulation of mitochondrial ROS generation and TGF-β1 activity
- PMID: 38413821
- PMCID: PMC10907606
- DOI: 10.1038/s12276-024-01170-w
Role of lung ornithine aminotransferase in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: regulation of mitochondrial ROS generation and TGF-β1 activity
Abstract
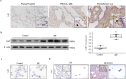
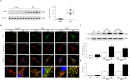
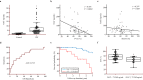
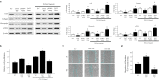
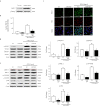
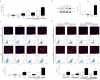
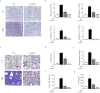
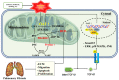
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is characterized by aberrant lung remodeling and the excessive accumulation of extracellular matrix (ECM) proteins. In a previous study, we found that the levels of ornithine aminotransferase (OAT), a principal enzyme in the proline metabolism pathway, were increased in the lungs of patients with IPF. However, the precise role played by OAT in the pathogenesis of IPF is not yet clear. The mechanism by which OAT affects fibrogenesis was assessed in vitro using OAT-overexpressing and OAT-knockdown lung fibroblasts. The therapeutic effects of OAT inhibition were assessed in the lungs of bleomycin-treated mice. OAT expression was increased in fibrotic areas, principally in interstitial fibroblasts, of lungs affected by IPF. OAT levels in the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid of IPF patients were inversely correlated with lung function. The survival rate was significantly lower in the group with an OAT level >75.659 ng/mL than in the group with an OAT level ≤75.659 ng/mL (HR, 29.53; p = 0.0008). OAT overexpression and knockdown increased and decreased ECM component production by lung fibroblasts, respectively. OAT knockdown also inhibited transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF)-β1 activity and TGF-β1 pathway signaling. OAT overexpression increased the generation of mitochondrial reactive oxygen species (ROS) by activating proline dehydrogenase. The OAT inhibitor L-canaline significantly attenuated bleomycin-induced lung injury and fibrosis. In conclusion, increased OAT levels in lungs affected by IPF contribute to the progression of fibrosis by promoting excessive mitochondrial ROS production, which in turn activates TGF-β1 signaling. OAT may be a useful target for treating patients with fibrotic lung diseases, including IPF.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Amifostine ameliorates bleomycin-induced murine pulmonary fibrosis via NAD+/SIRT1/AMPK pathway-mediated effects on mitochondrial function and cellular metabolism.Eur J Med Res. 2024 Jan 20;29(1):68. doi: 10.1186/s40001-023-01623-4. Eur J Med Res. 2024. PMID: 38245795 Free PMC article.
-
CCN5 overexpression inhibits profibrotic phenotypes via the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in lung fibroblasts isolated from patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and in an in vivo model of lung fibrosis.Int J Mol Med. 2014 Feb;33(2):478-86. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2013.1565. Epub 2013 Nov 25. Int J Mol Med. 2014. PMID: 24276150
-
miR-9-5p suppresses pro-fibrogenic transformation of fibroblasts and prevents organ fibrosis by targeting NOX4 and TGFBR2.EMBO Rep. 2015 Oct;16(10):1358-77. doi: 10.15252/embr.201540750. Epub 2015 Aug 27. EMBO Rep. 2015. PMID: 26315535 Free PMC article.
-
Sphingolipids in pulmonary fibrosis.Adv Biol Regul. 2015 Jan;57:55-63. doi: 10.1016/j.jbior.2014.09.008. Epub 2014 Oct 13. Adv Biol Regul. 2015. PMID: 25446881 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unraveling the interplay between vital organelle stress and oxidative stress in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2024 Mar;1871(3):119676. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2024.119676. Epub 2024 Jan 17. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2024. PMID: 38242330 Review.
Cited by
-
Gui-zhi-fu-ling-wan alleviates bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis through inhibiting epithelial-mesenchymal transition and ferroptosis.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Apr 16;16:1552251. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1552251. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40308766 Free PMC article.
-
Extra virgin olive oil mitigates lung injury in necrotizing enterocolitis: Effects on TGFβ1, Caspase-3, and MDA in a neonatal rat model.PLoS One. 2025 Apr 15;20(4):e0320938. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0320938. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40233022 Free PMC article.
-
Construction of mitochondrial signature (MS) for the prognosis of ovarian cancer.Discov Oncol. 2025 Jul 22;16(1):1388. doi: 10.1007/s12672-025-02892-7. Discov Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40694220 Free PMC article.
-
Deciphering the interplay: circulating cell-free DNA, signaling pathways, and disease progression in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.3 Biotech. 2025 Apr;15(4):102. doi: 10.1007/s13205-025-04272-y. Epub 2025 Mar 29. 3 Biotech. 2025. PMID: 40165930 Review.
-
Role of Arginine and its Metabolism in TGF-β-Induced Activation of Lung Fibroblasts.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Nov 1:2024.11.01.618293. doi: 10.1101/2024.11.01.618293. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 39554075 Free PMC article. Preprint.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

