Rapid, visual, label-based biosensor platform for identification of hepatitis C virus in clinical applications
- PMID: 38413863
- PMCID: PMC10900634
- DOI: 10.1186/s12866-024-03220-9
Rapid, visual, label-based biosensor platform for identification of hepatitis C virus in clinical applications
Abstract
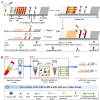
Objectives: In the current study, for the first time, we reported a novel HCV molecular diagnostic approach termed reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification integrated with a gold nanoparticles-based lateral flow biosensor (RT-LAMP-AuNPs-LFB), which we developed for rapid, sensitive, specific, simple, and visual identification of HCV.
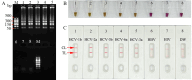
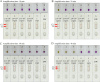
Methods: A set of LAMP primer was designed according to 5'untranslated region (5'UTR) gene from the major HCV genotypes 1b, 2a, 3b, 6a, and 3a, which are prevalent in China. The HCV-RT-LAMP-AuNPs-LFB assay conditions, including HCV-RT-LAMP reaction temperature and time were optimized. The sensitivity, specificity, and selectivity of our assay were evaluated in the current study. The feasibility of HCV-RT-LAMP-AuNPs-LFB was confirmed through clinical serum samples from patients with suspected HCV infections.
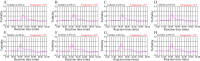
Results: An unique set of HCV-RT-LAMP primers were successfully designed targeting on the 5'UTR gene. The optimal detection process, including crude nucleic acid extraction (approximately 5 min), RT-LAMP reaction (67℃, 30 min), and visual interpretation of AuNPs-LFB results (~ 2 min), could be performed within 40 min without specific instruments. The limit of detection was determined to be 20 copies per test. The HCV-RT-LAMP-AuNPs-LFB assay exhibited high specificity and anti-interference.
Conclusions: These preliminary results confirmed that the HCV-RT-LAMP-AuNPs-LFB assay is a sensitive, specific, rapid, visual, and cost-saving assay for identification of HCV. This diagnostic approach has great potential value for point-of-care (POC) diagnostic of HCV, especially in resource-challenged regions.
Keywords: Biosensor; Hepatitis C virus; Limit of detection; Point-of-care platform; Reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Word Health Organization. WHO guidelines on hepatitis B and C testing. Geneva: World Health Organization;2017. Licence: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO. BY-NC-SA 3.0.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 2023KY995/the Medical Scientific Research Foundation of Zhejiang Province
- Qian Jiao Ji [2023]017/the Program of Key Laboratory of Higher Education in Guizhou Province
- zyyzdxk-2023187/the NATCM's Project of High-level Construction of Key TCM Disciplines
- gzwjkj2022-1-497/Program of Science and Technology of Guizhou Provincial Health Commission
- Qian Ke He Support [2023] General 242/the Guizhou Provincial Key Technology R&D Program
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

