Risk factors for falls in older adults with diabetes mellitus: systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 38413865
- PMCID: PMC10900672
- DOI: 10.1186/s12877-024-04668-0
Risk factors for falls in older adults with diabetes mellitus: systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Aim: To identify risk factors for falls in older adults with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM).
Methods: The eligible studies identified factors associated with the risk of falls in older adults with T2DM. We searched PubMed, Cinahl, Web of Science, Scopus, and the Cochrane Library databases. The review has been updated and the last review date was November 30, 2023 (CRD42020193461).
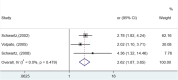
Results: Twelve studies met the inclusion criteria, and eight studies were included in the meta-analysis. These studies included a total of 40,778 older adults with T2DM, aged 60 to 101 years. The risk of developing the outcome falls in older adults with T2DM is 63% higher compared to the risk in older adults without T2DM (HR 1.63; 95% CI [1.30 - 2.05]). The overall chance of falling in older adults with T2DM is 59% higher than that of non-diabetic older adults (OR 1.59; 95% CI [1.36 -1.87]), and in older adults with T2DM who take insulin the chance of falling is 162% higher (OR 2.62; 95% CI [1.87 - 3.65]). No results on diabetic polyneuropathy were found in the studies.
Conclusion: Older adults with T2DM present a higher risk of falls compared to non-diabetics. Among the included older adults with T2DM, the most important factor associated with a higher risk of falls was insulin use.
Trial registration: Registered in the International Prospective Register of Systematic Reviews (CRD42020193461).
Keywords: Accidental falls; Falls; Older adults; Risk of falls; Type 2 diabetes mellitus.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Rachdaoui N. Insulin: the friend and the foe in the development of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Int J Mol Sci. 2020 [cited 2024 Jan 14];21(5):1770. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32150819/. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

