Trends in orphan medicinal products approvals in the European Union between 2010-2022
- PMID: 38413985
- PMCID: PMC10900541
- DOI: 10.1186/s13023-024-03095-z
Trends in orphan medicinal products approvals in the European Union between 2010-2022
Abstract
Background: Over the last twenty years of orphan drug regulation in Europe, the regulatory framework has increased its complexity, with different regulatory paths and tools engineered to facilitate the innovation and accelerate approvals. Recently, the proposal of the new Pharmaceutical Legislation for the European Union, which will replace at least three Regulations and one Directive, was released and its new framework is raising many questions. The aim of this study was to present a characterisation of the Orphan Medicinal Products (OMPs) authorised by the European Commission (EC), between 2010 and 2022, looking into eighteen variables, contributing to the ongoing discussion on the proposal and implementation of the new Pharmaceutical Legislation proposed.
Methods: Data of the OMPs identified and approved between 2010 and 2022 were extracted from the European Public Assessment Reports (EPARs) produced by the European Medicines Agency. Information regarding legal basis of the application, applicant, protocol assistance received, type of authorization, registration status, type of molecule, ATC code, therapeutic area, target age, disease prevalence, number of pivotal clinical trials supporting the application, clinical trial designs, respective efficacy endpoints and number of patients enrolled in the pivotal clinical trials were extracted. A descriptive statistical analysis was applied.
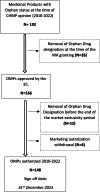
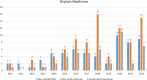
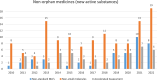
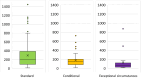
Results: We identified 192 OMPs approved in the period between 2010 and 2022. 89% of the OMPs have legal basis of "full application". 86% of the sponsors received protocol assistance whereas 64% of the MAA benefited from the accelerated assessment. 53% of the active substances are small molecules; about 1 in 5 molecules are repurposed. 40% of the OMPs have oncological therapeutic indications and 56% of the OMPs are intended to treat only adults. 71% of the products were approved based on a single pivotal trial.
Conclusions: This analysis of OMPs approved between 2010 and 2022 shows that a shift has occurred in the rare disease medicine development space. Through the period studied we observe an increase of non-small molecules approved, accelerated assessment received and non-standard MA's granted.
Keywords: Accelerated assessment; Incentives; Orphan medicines; Orphan regulation; Rare diseases.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Regulation (EC) No 141/2000 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 16 December 1999 on orphan medicinal products. Official Journal of the European Union. 2000;L 18:1–5.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

