Factors influencing the use of natural health products, in particular for concentration and cognition in Germany
- PMID: 38414023
- PMCID: PMC10898047
- DOI: 10.1186/s12906-024-04407-3
Factors influencing the use of natural health products, in particular for concentration and cognition in Germany
Abstract
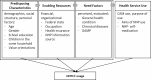
Background: Natural health products (NHP) are an important part of the healthcare system. They are mainly non-prescription and sold over the counter, which requires active decision making by the consumer. Within the framework of the Complementary and Alternative Healthcare Model, this study aims to identify factors that influence NHP usage, in particular related to concentration and cognition (CC), a topic that concerns all ages and social classes within the population.
Methods: Data were collected by means of a representative online survey (n = 1,707) in Germany in April 2022. Three user groups were defined: NHPCC users, who used NHP for CC (12 month prevalence); nCC-NHP users, who used NHP but not for CC indications (12 month prevalence); and past NHP users, who have used NHP but not within the previous 12 months. Independent influencing variables were categorized into predisposing, enabling, need, and health service use factors. Data were analyzed with descriptive statistics, inferential statistics, and binary logistic regression models to compare NHPCC users to nCC-NHP users (model 1) and to past NHP users (model 2).
Results: A higher share of NHPCC and nCC-NHP users compared to past NHP users were women, self-medicated with NHP, and used information about NHP provided by health professionals or on product. Their openness-to-change value orientation was more pronounced than of past users. Compared to nCC-NHP and past NHP users, the probability of being an NHPCC user increased if an individual had more difficulties in daily attention and memory performance, made use of health professionals and literature to seek information about NHP, and used NHP for health support and illness prevention. Additionally, a female gender, NHP self-medication, and having higher values of self-transcendence were significant indicators for NHPCC usage compared to past NHP usage.
Conclusion: NHP manufacturers, health professionals, and policymakers should be aware of the factors that lead to NHP consumption decisions and consider them in the development and optimization of healthcare strategies as well as in the marketing and communication strategies of companies producing NHP, in particular for CC. The current study can contribute to characterizing the target groups and to defining the aims and communication channels of such campaigns.
Keywords: CAM healthcare model; Concentration and cognition; Decision making; Natural health product; Value orientation.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Ganesan A. The impact of natural products upon modern drug discovery. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2008;12(3):306–17. - PubMed
-
- Eardley S, Bishop FL, Prescott P, Cardini F, Brinkhaus B, Santos-Rey K, Vas J, Ammon Kv, Hegyi G, Dragan S, Uehleke B, Fønnebø V, Lewith G. A systematic literature review of complementary and alternative medicine prevalence in EU. Complement Med Res. 2012;19(2):18–28. - PubMed
-
- Thakkar S, Anklam E, Xu A, Ulberth F, Li J, Li B, Hugas M, Sarma N, Crerar S, Swift S, Hakamatsuka T, Curtui V, Yan W, Geng X, Slikker W, Tong W. Regulatory landscape of dietary supplements and herbal medicines from a global perspective. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol. 2020;114:104647. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous