Inhibition of Gpx4-mediated ferroptosis alleviates cisplatin-induced hearing loss in C57BL/6 mice
- PMID: 38414247
- PMCID: PMC11081921
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2024.02.029
Inhibition of Gpx4-mediated ferroptosis alleviates cisplatin-induced hearing loss in C57BL/6 mice
Abstract
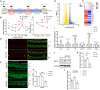
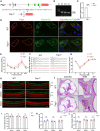
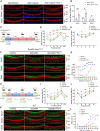
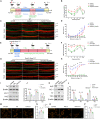
Cisplatin-induced hearing loss is a common side effect of cancer chemotherapy in clinics; however, the mechanism of cisplatin-induced ototoxicity is still not completely clarified. Cisplatin-induced ototoxicity is mainly associated with the production of reactive oxygen species, activation of apoptosis, and accumulation of intracellular lipid peroxidation, which also is involved in ferroptosis induction. In this study, the expression of TfR1, a ferroptosis biomarker, was upregulated in the outer hair cells of cisplatin-treated mice. Moreover, several key ferroptosis regulator genes were altered in cisplatin-damaged cochlear explants based on RNA sequencing, implying the induction of ferroptosis. Ferroptosis-related Gpx4 and Fsp1 knockout mice were established to investigate the specific mechanisms associated with ferroptosis in cochleae. Severe outer hair cell loss and progressive damage of synapses in inner hair cells were observed in Atoh1-Gpx4-/- mice. However, Fsp1-/- mice showed no significant hearing phenotype, demonstrating that Gpx4, but not Fsp1, may play an important role in the functional maintenance of HCs. Moreover, findings showed that FDA-approved luteolin could specifically inhibit ferroptosis and alleviate cisplatin-induced ototoxicity through decreased expression of transferrin and intracellular concentration of ferrous ions. This study indicated that ferroptosis inhibition through the reduction of intracellular ferrous ions might be a potential strategy to prevent cisplatin-induced hearing loss.
Keywords: Fsp1; Gpx4; cisplatin-induced ototoxicity; ferroptosis; luteolin; transferrin.
Copyright © 2024. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Coen J.J., Zhang P., Saylor P.J., Lee C.T., Wu C.L., Parker W., Lautenschlaeger T., Zietman A.L., Efstathiou J.A., Jani A.B., et al. Bladder Preservation With Twice-a-Day Radiation Plus Fluorouracil/Cisplatin or Once Daily Radiation Plus Gemcitabine for Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer: NRG/RTOG 0712A Randomized Phase II Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019;37:44–51. doi: 10.1200/Jco.18.00537. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Du J., Wang X., Li Y., Ren X., Zhou Y., Hu W., Zhou C., Jing Q., Yang C., Wang L., et al. DHA exhibits synergistic therapeutic efficacy with cisplatin to induce ferroptosis in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma via modulation of iron metabolism. Cell Death Dis. 2021;12 doi: 10.1038/s41419-021-03996-y. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

