Activation of the YAP/KLF5 transcriptional cascade in renal tubular cells aggravates kidney injury
- PMID: 38414248
- PMCID: PMC11081877
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2024.02.031
Activation of the YAP/KLF5 transcriptional cascade in renal tubular cells aggravates kidney injury
Abstract
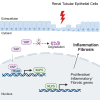
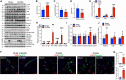
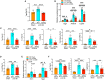
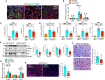
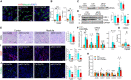
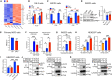
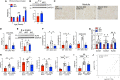
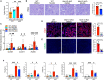
The Hippo/YAP pathway plays a critical role in tissue homeostasis. Our previous work demonstrated that renal tubular YAP activation induced by double knockout (dKO) of the upstream Hippo kinases Mst1 and Mst2 promotes tubular injury and renal inflammation under basal conditions. However, the importance of tubular YAP activation remains to be established in injured kidneys in which many other injurious pathways are simultaneously activated. Here, we show that tubular YAP was already activated 6 h after unilateral ureteral obstruction (UUO). Tubular YAP deficiency greatly attenuated tubular cell overproliferation, tubular injury, and renal inflammation induced by UUO or cisplatin. YAP promoted the transcription of the transcription factor KLF5. Consistent with this, the elevated expression of KLF5 and its target genes in Mst1/2 dKO or UUO kidneys was blocked by ablation of Yap in tubular cells. Inhibition of KLF5 prevented tubular cell overproliferation, tubular injury, and renal inflammation in Mst1/2 dKO kidneys. Therefore, our results demonstrate that tubular YAP is a key player in kidney injury. YAP and KLF5 form a transcriptional cascade, where tubular YAP activation induced by kidney injury promotes KLF5 transcription. Activation of this cascade induces tubular cell overproliferation, tubular injury, and renal inflammation.
Keywords: Hippo; KLF5; MST1; MST2; UUO; YAP; kidney; tubular injury.
Copyright © 2024 The American Society of Gene and Cell Therapy. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Humphreys B.D. Mechanisms of Renal Fibrosis. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2018;80:309–326. - PubMed
-
- Levin A. Global challenges in kidney diseases. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2018;33:371–372. - PubMed
-
- Zhang L., Wang F., Wang L., Wang W., Liu B., Liu J., Chen M., He Q., Liao Y., Yu X., et al. Prevalence of chronic kidney disease in China: a cross-sectional survey. Lancet. 2012;379:815–822. - PubMed
-
- Liu B.C., Tang T.T., Lv L.L., Lan H.Y. Renal tubule injury: a driving force toward chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2018;93:568–579. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

