Liver sinusoidal endothelial cell: An important yet often overlooked player in the liver fibrosis
- PMID: 38414375
- PMCID: PMC11261236
- DOI: 10.3350/cmh.2024.0022
Liver sinusoidal endothelial cell: An important yet often overlooked player in the liver fibrosis
Abstract
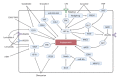
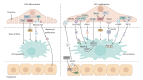
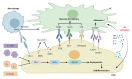
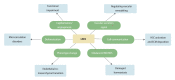
Liver sinusoidal endothelial cells (LSECs) are liver-specific endothelial cells with the highest permeability than other mammalian endothelial cells, characterized by the presence of fenestrae on their surface, the absence of diaphragms and the lack of basement membrane. Located at the interface between blood and other liver cell types, LSECs mediate the exchange of substances between the blood and the Disse space, playing a crucial role in maintaining substance circulation and homeostasis of multicellular communication. As the initial responders to chronic liver injury, the abnormal LSEC activation not only changes their own physicochemical properties but also interrupts their communication with hepatic stellate cells and hepatocytes, which collectively aggravates the process of liver fibrosis. In this review, we have comprehensively updated the various pathways by which LSECs were involved in the initiation and aggravation of liver fibrosis, including but not limited to cellular phenotypic change, the induction of capillarization, decreased permeability and regulation of intercellular communications. Additionally, the intervention effects and latest regulatory mechanisms of anti-fibrotic drugs involved in each aspect have been summarized and discussed systematically. As we studied deeper into unraveling the intricate role of LSECs in the pathophysiology of liver fibrosis, we unveil a promising horizon that pave the way for enhanced patient outcomes.
Keywords: Capillarization; Fenestrae; Intercellular communication; Liver fibrosis; Liver sinusoidal endothelial cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Comment in
-
Unlocking the role of liver sinusoidal endothelial cells: Key players in liver fibrosis: Editorial on "Liver sinusoidal endothelial cell: An important yet often overlooked player in the liver fibrosis".Clin Mol Hepatol. 2024 Oct;30(4):673-676. doi: 10.3350/cmh.2024.0343. Epub 2024 May 10. Clin Mol Hepatol. 2024. PMID: 38726502 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Liver sinusoidal endothelial cells in hepatic fibrosis: opportunities for future strategies.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2025 Jun 20;766:151881. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2025.151881. Epub 2025 Apr 23. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2025. PMID: 40286764 Review.
-
Delta-like ligand 4/DLL4 regulates the capillarization of liver sinusoidal endothelial cell and liver fibrogenesis.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2019 Oct;1866(10):1663-1675. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2019.06.011. Epub 2019 Jun 21. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2019. PMID: 31233801
-
Liver Sinusoidal Endothelial Cells in the Regulation of Immune Responses and Fibrosis in Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Apr 23;26(9):3988. doi: 10.3390/ijms26093988. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40362227 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Liver X receptor α is essential for the capillarization of liver sinusoidal endothelial cells in liver injury.Sci Rep. 2016 Feb 18;6:21309. doi: 10.1038/srep21309. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 26887957 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction of non‑parenchymal hepatocytes in the process of hepatic fibrosis (Review).Mol Med Rep. 2021 May;23(5):364. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2021.12003. Epub 2021 Mar 24. Mol Med Rep. 2021. PMID: 33760176 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Unlocking the role of liver sinusoidal endothelial cells: Key players in liver fibrosis: Editorial on "Liver sinusoidal endothelial cell: An important yet often overlooked player in the liver fibrosis".Clin Mol Hepatol. 2024 Oct;30(4):673-676. doi: 10.3350/cmh.2024.0343. Epub 2024 May 10. Clin Mol Hepatol. 2024. PMID: 38726502 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Anogeissus leiocarpus (DC.) Guill. & Perr. extract-protected rats against CCl4-induced liver fibrosis.J Taibah Univ Med Sci. 2025 Jul 31;20(4):474-486. doi: 10.1016/j.jtumed.2025.07.003. eCollection 2025 Aug. J Taibah Univ Med Sci. 2025. PMID: 40792255 Free PMC article.
-
Injury and Fibrosis at the Myoaponeurotic Junction of Pectoralis Major and Supracoracoideus Muscles in Broiler Chickens.J Poult Sci. 2025 Apr 5;62:2025014. doi: 10.2141/jpsa.2025014. eCollection 2025. J Poult Sci. 2025. PMID: 40190448 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome Analyses of Liver Sinusoidal Endothelial Cells Reveal a Consistent List of Candidate Genes Associated with Endothelial Dysfunction and the Fibrosis Progression.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024 Jul 25;46(8):7997-8014. doi: 10.3390/cimb46080473. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 39194690 Free PMC article.
-
Correspondence to editorial on "Liver sinusoidal endothelial cell: An important yet often overlooked player in the liver fibrosis".Clin Mol Hepatol. 2024 Oct;30(4):1002-1004. doi: 10.3350/cmh.2024.0357. Epub 2024 May 17. Clin Mol Hepatol. 2024. PMID: 38755017 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Parola M, Pinzani M. Liver fibrosis: Pathophysiology, pathogenetic targets and clinical issues. Mol Aspects Med. 2019;65:37–55. - PubMed
-
- Hammerich L, Tacke F. Hepatic inflammatory responses in liver fibrosis. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2023;20:633–646. - PubMed
-
- Kisseleva T, Brenner D. Molecular and cellular mechanisms of liver fibrosis and its regression. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021;18:151–166. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

