Evaluation of a deep learning magnetic resonance imaging reconstruction method for synthetic computed tomography generation in prostate radiotherapy
- PMID: 38414521
- PMCID: PMC10897922
- DOI: 10.1016/j.phro.2024.100557
Evaluation of a deep learning magnetic resonance imaging reconstruction method for synthetic computed tomography generation in prostate radiotherapy
Abstract
Background and purpose: In magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) only radiotherapy computed tomography (CT) is excluded. The method relies entirely on synthetic CT images generated from MRI. This study evaluates the compatibility of a commercial synthetic CT (sCT) with an accelerated commercial deep learning reconstruction (DLR) in MRI-only prostate radiotherapy.
Materials and methods: For a group of 24 patients (cohort 1) the effects of DLR were studied in isolation. MRI data were reconstructed conventionally and with DLR from identical k-space data, and sCTs were generated for both reconstructions. The sCT quality, Hounsfield Unit (HU) and dosimetric impact were investigated. In another group of 15 patients (cohort 2) effects on sCT generation using accelerated MRI acquisition (40 % time reduction) reconstructed with DLR were investigated.
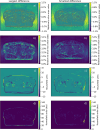
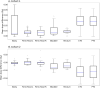
Results: sCT images from both cohorts, generated from DLR MRI data, were of clinically expected image quality. The mean dose differences for targets and organs at risks in cohort 1 were <0.06 Gy, corresponding to a 0.1 % prescribed dose difference. Similar dose differences were observed in cohort 2. Gamma pass rates for cohort 1 were 100 % for criteria 3 %/3mm, 2 %/2mm and 1 %/1mm for all dose levels. Mean error and mean absolute error inside the body, between sCTs, averaged over all cohort 1 subjects, were -1.1 ± 0.6 [-2.4 0.2] and 2.9 ± 0.4 [2.3 3.9] HU, respectively.
Conclusions: DLR was suitable for sCT generation with clinically negligible differences in HU and calculated dose compared to the conventional MRI reconstruction method. For sCT generation DLR enables scan time reduction, without compromised sCT quality.
Keywords: Deep learning reconstruction; MRI; Prostate cancer; Radiotherapy; Synthetic CT.
© 2024 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following financial interests/personal relationships which may be considered as potential competing interests: CJG has received a speaker fee from GE Healthcare. Other authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Evaluating the Hounsfield unit assignment and dose differences between CT-based standard and deep learning-based synthetic CT images for MRI-only radiation therapy of the head and neck.J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2024 Jan;25(1):e14239. doi: 10.1002/acm2.14239. Epub 2023 Dec 21. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2024. PMID: 38128040 Free PMC article.
-
Dosimetric evaluation of synthetic CT for head and neck radiotherapy generated by a patch-based three-dimensional convolutional neural network.Med Phys. 2019 Sep;46(9):4095-4104. doi: 10.1002/mp.13663. Epub 2019 Jul 9. Med Phys. 2019. PMID: 31206701
-
Comparison of Synthetic Computed Tomography Generation Methods, Incorporating Male and Female Anatomical Differences, for Magnetic Resonance Imaging-Only Definitive Pelvic Radiotherapy.Front Oncol. 2022 Feb 8;12:822687. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.822687. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35211413 Free PMC article.
-
Deep learning MRI-only synthetic-CT generation for pelvis, brain and head and neck cancers.Radiother Oncol. 2024 Feb;191:110052. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2023.110052. Epub 2023 Dec 12. Radiother Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38096921
-
Deep learning methods to generate synthetic CT from MRI in radiotherapy: A literature review.Phys Med. 2021 Sep;89:265-281. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmp.2021.07.027. Epub 2021 Aug 30. Phys Med. 2021. PMID: 34474325 Review.
Cited by
-
Impact of deep learning model uncertainty on manual corrections to MRI-based auto-segmentation in prostate cancer radiotherapy.J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2025 Sep;26(9):e70221. doi: 10.1002/acm2.70221. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2025. PMID: 40849835 Free PMC article.
-
Results of 2023 survey on the use of synthetic computed tomography for magnetic resonance Imaging-only radiotherapy: Current status and future steps.Phys Imaging Radiat Oncol. 2024 Sep 26;32:100652. doi: 10.1016/j.phro.2024.100652. eCollection 2024 Oct. Phys Imaging Radiat Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39381612 Free PMC article.
-
LUND-PROBE - LUND Prostate Radiotherapy Open Benchmarking and Evaluation dataset.Sci Data. 2025 Apr 11;12(1):611. doi: 10.1038/s41597-025-04954-5. Sci Data. 2025. PMID: 40216786 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Johnstone E., Wyatt J.J., Henry A.M., Short S.C., Sebag-Montefiore D., Murray L., et al. Systematic review of synthetic computed tomography generation methodologies for use in magnetic resonance imaging-only radiation therapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2018;100:199–217. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2017.08.043. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Lebel RM. Performance characterization of a novel deep learning-based MR image reconstruction pipeline. arXiv preprint arXiv:2008.06559 2020. Doi:10.48550/arXiv.2008.06559.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

