Combined Photosensitive Gene Therapy Effective Against Triple-Negative Breast Cancer in Mice Model
- PMID: 38414523
- PMCID: PMC10898360
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S449042
Combined Photosensitive Gene Therapy Effective Against Triple-Negative Breast Cancer in Mice Model
Abstract
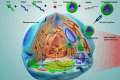
Introduction: Tumor hypoxia and invasion present significant challenges for the efficacy of photodynamic therapy (PDT) in triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC). This study developed a mitochondrial targeting strategy that combined PDT and gene therapy to promote each other and address the challenges.
Methods: The positively charged amphiphilic material triphenylphosphine-tocopherol polyethylene glycol succinate (TPP-TPGS, TPS) and the photosensitizer chloride e6 (Ce6) formed TPS@Ce6 nanoparticles (NPs) by hydrophobic interaction. They electrostatically condensed microRNA-34a (miR-34a) to form stable TPS@Ce6/miRNA NPs.
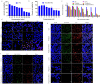
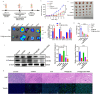
Results: Firstly, Ce6 disrupted the lysosomal membrane, followed by successful delivery of miR-34a by TPS@Ce6/miRNA NPs. Meanwhile, miR-34a reduced ROS depletion and further enhanced the effectiveness of PDT. Consequently, the mutual promotion between PDT and gene therapy led to enhanced anti-tumor effects. Furthermore, the TPS@Ce6/miRNA NPs promoted apoptosis by down-regulating Caspase-3 and inhibited tumor cell migration and invasion by down-regulating N-Cadherin. In addition, in vitro and in vivo experiments demonstrated that the TPS@Ce6/miRNA NPs achieved excellent anti-tumor effects. These findings highlighted the enhanced anticancer effects and reduced migration of tumor cells through the synergistic effects of PDT and gene therapy.
Conclusion: Taken together, the targeted co-delivery of Ce6 and miR-34a will facilitate the application of photodynamic and genic nanomedicine in the treatment of aggressive tumors, particularly TNBC.
Keywords: gene therapy; hypoxia; invasion; mitochondrial target; photodynamic therapy; triple-negative breast cancer.
© 2024 Hu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

