A review on regulation of DNA methylation during post-myocardial infarction
- PMID: 38414735
- PMCID: PMC10896928
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1267585
A review on regulation of DNA methylation during post-myocardial infarction
Abstract
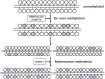
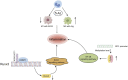
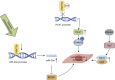
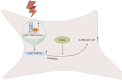
Myocardial infarction (MI) imposes a huge medical and economic burden on society, and cardiac repair after MI involves a complex series of processes. Understanding the key mechanisms (such as apoptosis, autophagy, inflammation, and fibrosis) will facilitate further drug development and patient treatment. Presently, a substantial body of evidence suggests that the regulation of epigenetic processes contributes to cardiac repair following MI, with DNA methylation being among the notable epigenetic factors involved. This article will review the research on the mechanism of DNA methylation regulation after MI to provide some insights for future research and development of related drugs.
Keywords: DNA methylation; autophagy; fibrosis; inflammation; myocardial infarction; proliferation.
Copyright © 2024 Han, Wang, Wang, Maduray, Hao and Zhong.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Bajpai G., Bredemeyer A., Li W., Zaitsev K., Koenig A. L., Lokshina I., et al. (2019). Tissue resident CCR2-and CCR2+ cardiac macrophages differentially orchestrate monocyte recruitment and fate specification following myocardial injury. Circulation Res. 124 (2), 263–278. 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.118.314028 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Balasubramanian A., Kawahara G., Gupta V. A., Rozkalne A., Beauvais A., Kunkel L. M., et al. (2014). Fam65b is important for formation of the HDAC6-dysferlin protein complex during myogenic cell differentiation. FASEB J. official Publ. Fed. Am. Soc. Exp. Biol. 28 (7), 2955–2969. 10.1096/fj.13-246470 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

