Challenges in treating children with optic pathway gliomas: an 18-year experience from a middle-income country
- PMID: 38414749
- PMCID: PMC10898851
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1329729
Challenges in treating children with optic pathway gliomas: an 18-year experience from a middle-income country
Abstract
Introduction: Patients with optic pathway gliomas (OPG) have good survival rates although their long-term quality of life can be affected by the tumor or treatment-related morbidity. This retrospective study sought to describe the clinical presentation and outcomes of children with OPG at a tertiary center in Mexico.
Methods: Consecutive patients <18 years-of-age with newly diagnosed OPG between January 2002 and December 2020 at the Hospital Civil de Guadalajara Dr. Juan I. Menchaca in Guadalajara, Mexico were included.
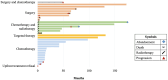
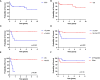
Results: Thirty patients were identified with a median age of six years. The most frequent clinical manifestations were loss of visual acuity (40%) and headaches (23%). Neurofibromatosis-1 was found in 23.3% of the patients. Surgery, either biopsy or resection, was done in 20 of 30 patients. Two patients died shortly after initial surgery. The 5-year event-free survival (EFS) was 79.3% ± 10.8% and the 5-year overall survival was 89.5% ± 6.9%. Lower EFS was associated with age less than 3 years, intracranial hypertension at presentation, and diencephalic syndrome. Patients who received surgery as first-line treatment had a 3.1 times greater risk of achieving a performance score of less than 90 points at 6 months after diagnosis (p=0.006). Of 10 patients with vision testing, 5 had improvement in visual acuity, 4 had no changes, and one patient showed worsening.
Conclusion: Our data suggests that favorable outcomes can be achieved with OPG in low- and middle-income countries, although a high rate of surgical complications was described leading to a lower overall survival. These data can be used prospectively to optimize treatment at this institute and other middle-income countries through a comprehensive, multidisciplinary approach.
Keywords: global oncology; low-and middle-income countries; low-grade glioma; optic pathway glioma; visual acuity.
Copyright © 2024 Ramírez-Melo, Moreira, Orozco-Alvarado, Sánchez-Zubieta and Navarro-Martín del Campo.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

