Whipple's disease of the respiratory system: A case report
- PMID: 38414785
- PMCID: PMC10895612
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2024.12421
Whipple's disease of the respiratory system: A case report
Abstract
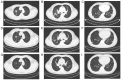
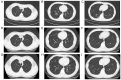
Whipple's disease (WD) is a multiple-system chronic disease caused by Tropheryma whipplei (T. whipplei) infection. The present study describes 3 cases of WD with clinical manifestations of cough, chest pain, headache, dyspnea, sputum, joint pain, abdominal pain, diarrhea and weight loss. Chest computed tomography (CT) showed signs of plaques, nodules and pleural thickening; and bronchoscopic alveolar lavage fluid metagenomic-sequencing indicated that it was T. whipplei. One patient was treated with meropenem as the starting regimen and two patients were treated with ceftriaxone as the starting regimen. Furthermore, two patients were provided with a maintenance regimen of cotrimoxazole and one was given a maintenance regimen of minocycline, which was combined with meropenem and ceftriaxone in order to improve their cough, chest pain, headache and dyspnea symptoms. To the best of our knowledge, there are few reports on WD of the respiratory system caused by T. whipplei, and differential diagnosis is the key to clinical diagnosis. When WD of the respiratory system is difficult to diagnose, metagenomic second-generation sequencing (mNGS) may be a better choice, which can achieve early diagnosis and early treatment. However, its clinical value is still limited; therefore, more research needs to be conducted in the future.
Keywords: Tropheryma whipplei; Whipple's disease; case report; metagenomic second-generation sequencing; respiratory system.
Copyright: © Deng et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Tropheryma whipplei detection by metagenomic next-generation sequencing in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid: A cross-sectional study.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022 Aug 17;12:961297. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.961297. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36061864 Free PMC article.
-
Pulmonary parenchymal involvement caused by Tropheryma whipplei.Open Med (Wars). 2021 Jun 2;16(1):843-846. doi: 10.1515/med-2021-0297. eCollection 2021. Open Med (Wars). 2021. PMID: 34131590 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnosis and treatment of Whipple disease after kidney transplantation: A case report.World J Clin Cases. 2023 Sep 6;11(25):6019-6024. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i25.6019. World J Clin Cases. 2023. PMID: 37727483 Free PMC article.
-
[Tropheryma whipplei infection. Colonization, self-limiting infection and Whipple's disease].Pathologe. 2011 Sep;32(5):362-70. doi: 10.1007/s00292-011-1446-y. Pathologe. 2011. PMID: 21667114 Review. German.
-
Whipple's disease.J Neurol Sci. 2017 Jun 15;377:197-206. doi: 10.1016/j.jns.2017.01.048. Epub 2017 Feb 16. J Neurol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28477696 Review.
Cited by
-
From Symptoms to Solution: A Diagnostic Challenge of Whipple's Disease.Cureus. 2025 Apr 5;17(4):e81767. doi: 10.7759/cureus.81767. eCollection 2025 Apr. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40330368 Free PMC article.
-
A Rare Case Report of Tropheryma Whipplei-Induced Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome in an Immunocompetent Patient.Infect Drug Resist. 2025 Jul 8;18:3409-3414. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S530544. eCollection 2025. Infect Drug Resist. 2025. PMID: 40657275 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
