Investigation of vagal sensory neurons in mice using optical vagal stimulation and tracheal neuroanatomy
- PMID: 38414860
- PMCID: PMC10897902
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.109182
Investigation of vagal sensory neurons in mice using optical vagal stimulation and tracheal neuroanatomy
Abstract
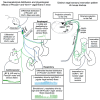
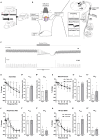
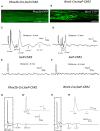
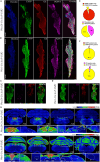
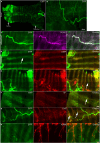
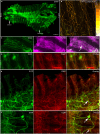
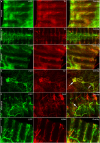
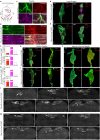
In rats and guinea pigs, sensory innervation of the airways is derived largely from the vagus nerve, with the extrapulmonary airways innervated by Wnt1+ jugular neurons and the intrapulmonary airways and lungs by Phox2b+ nodose neurons; however, our knowledge of airway innervation in mice is limited. We used genetically targeted expression of enhanced yellow fluorescent protein-channelrhodopsin-2 (EYFP-ChR2) in Wnt1+ or Phox2b+ tissues to characterize jugular and nodose-mediated physiological responses and airway innervation in mice. With optical stimulation, Phox2b+ vagal fibers modulated cardiorespiratory function in a frequency-dependent manner while right Wnt1+ vagal fibers induced a small increase in respiratory rate. Mouse tracheae contained sparse Phox2b-EYFP fibers but dense networks of Wnt1-EYFP fibers. Retrograde tracing from the airways showed limited tracheal innervation by the jugular sensory neurons, distinct from other species. These differences in physiology and vagal sensory distribution have important implications when using mice for studying airway neurobiology.
Keywords: Sensory neuroscience; Techniques in neuroscience.
© 2024 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
S.B.M. reports receiving grants from Merck, Bellus Health and Reckitt Benkiser, and remuneration for consultancy from Merck, Bellus Health, Reckitt Benkiser and Nerre Therapeutics and has served on advisory committees for Merck, Reckitt Benkiser and Trevi Therapeutics, all of which are unrelated to the contents of the current manuscript.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Descending Modulation of Laryngeal Vagal Sensory Processing in the Brainstem Orchestrated by the Submedius Thalamic Nucleus.J Neurosci. 2020 Dec 2;40(49):9426-9439. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2430-20.2020. Epub 2020 Oct 28. J Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 33115928 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of the Paratrigeminal Nucleus in Vagal Afferent Evoked Respiratory Reflexes: A Neuroanatomical and Functional Study in Guinea Pigs.Front Physiol. 2015 Dec 21;6:378. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2015.00378. eCollection 2015. Front Physiol. 2015. PMID: 26733874 Free PMC article.
-
Neurotrophin and GDNF family ligand receptor expression in vagal sensory nerve subtypes innervating the adult guinea pig respiratory tract.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2011 May;300(5):L790-8. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00449.2010. Epub 2011 Feb 18. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21335521 Free PMC article.
-
Jugular vagal ganglia neurons and airway nociception: A target for treating chronic cough.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2021 Jun;135:105981. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2021.105981. Epub 2021 Apr 22. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2021. PMID: 33895353 Review.
-
Vagal Afferent Innervation of the Airways in Health and Disease.Physiol Rev. 2016 Jul;96(3):975-1024. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00039.2015. Physiol Rev. 2016. PMID: 27279650 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Cracking the Code of the Jugular Vagal Sensory Neurons in Allergic Airway Responsiveness.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2025 Apr;72(4):346-348. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2024-0445ED. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 39471332 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Evidence for vagal sensory neural involvement in influenza pathogenesis and disease.PLoS Pathog. 2024 Apr 16;20(4):e1011635. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1011635. eCollection 2024 Apr. PLoS Pathog. 2024. PMID: 38626267 Free PMC article.
-
MrgprC11+ Jugular Neurons Control Airway Hyperresponsiveness in Allergic Airway Inflammation.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2025 Apr;72(4):393-407. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2024-0153OC. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 39405479
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

